With my case, I want to win a #ITIWS24freeticket to attend the ITI World Symposium 2024 from May 9-11 for free
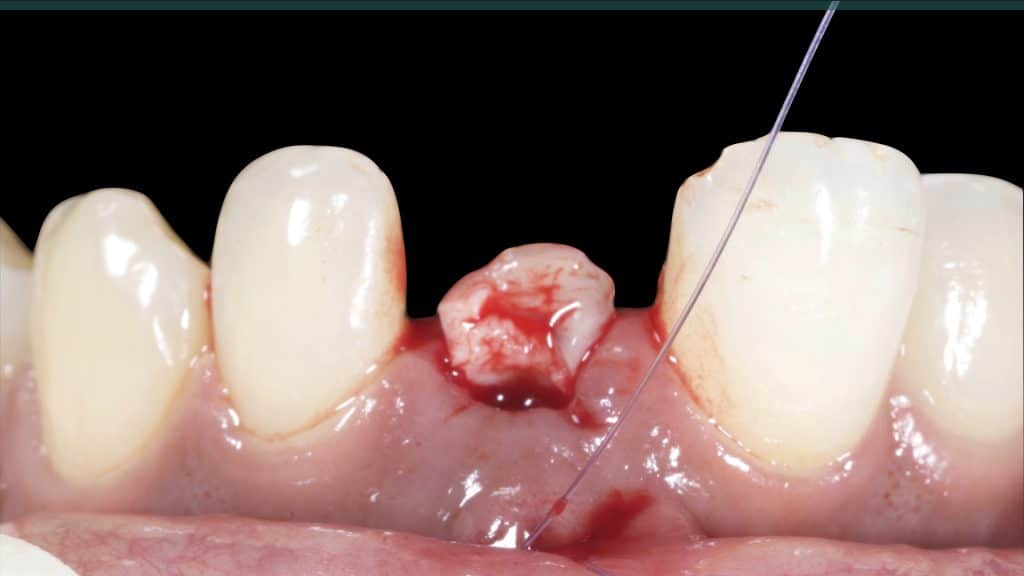
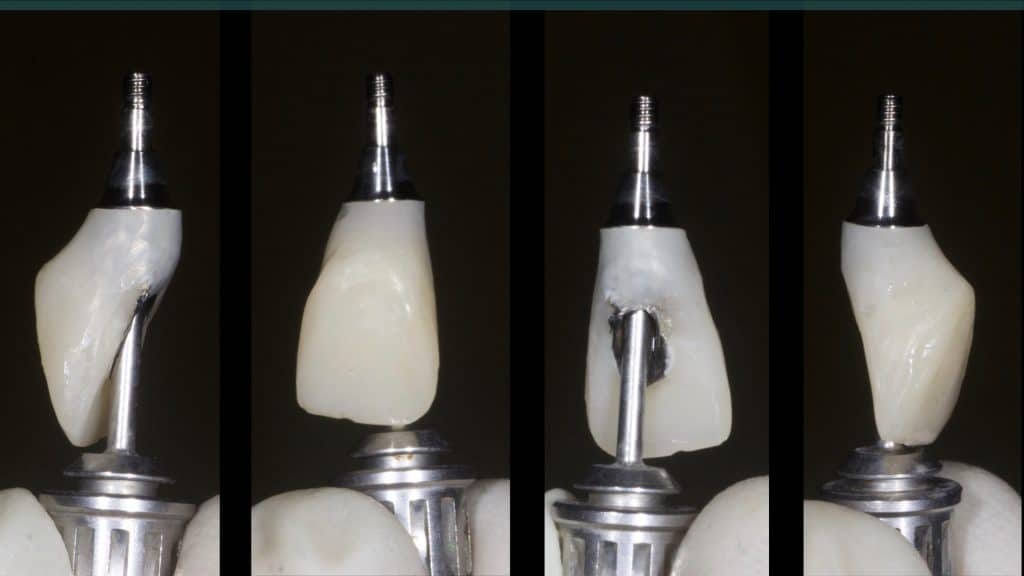
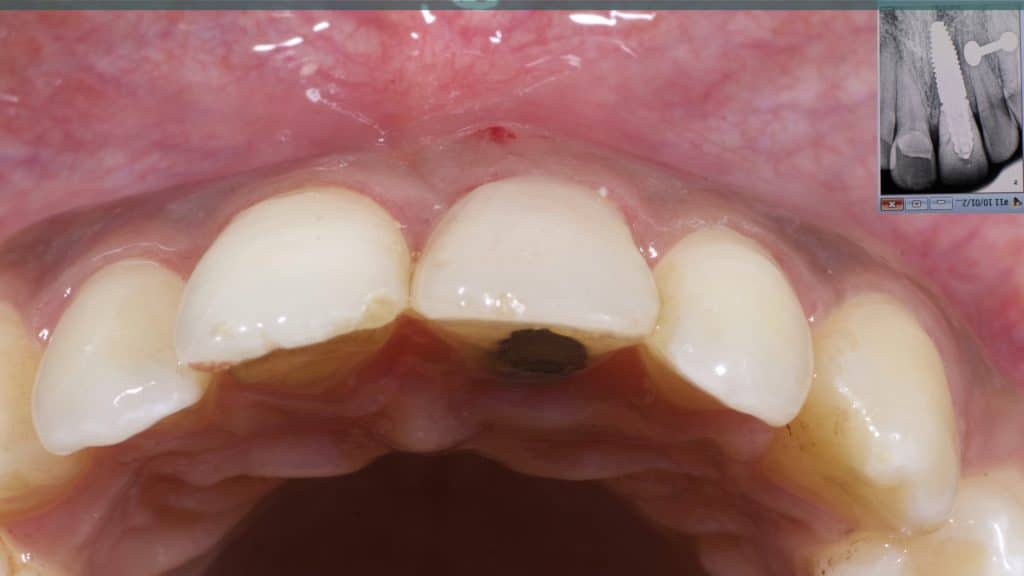
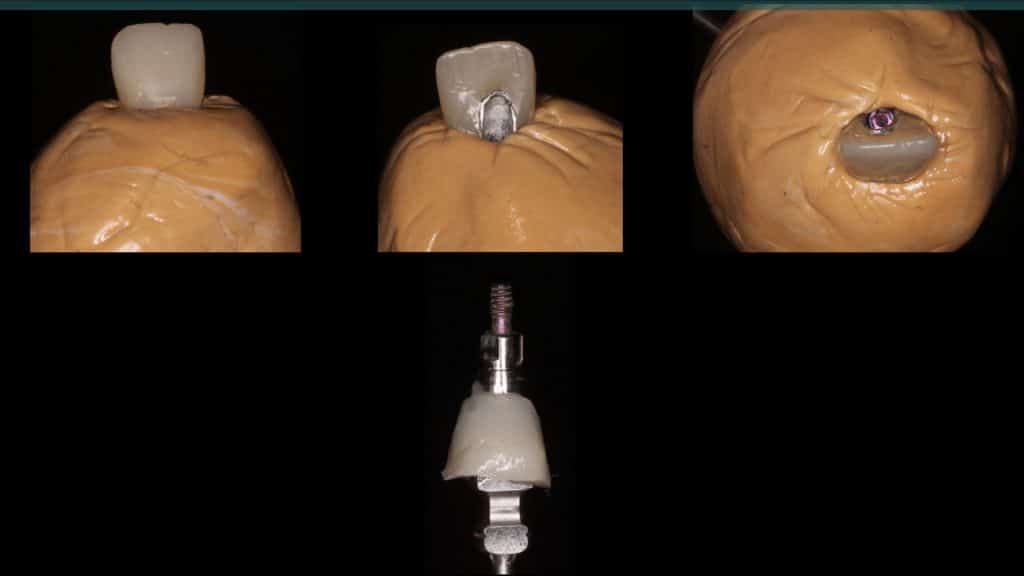
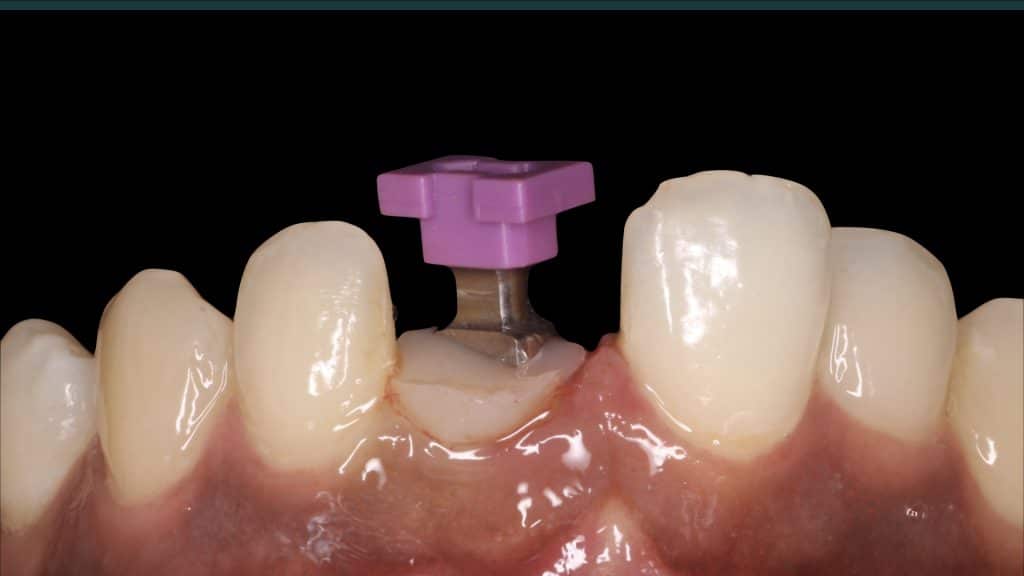
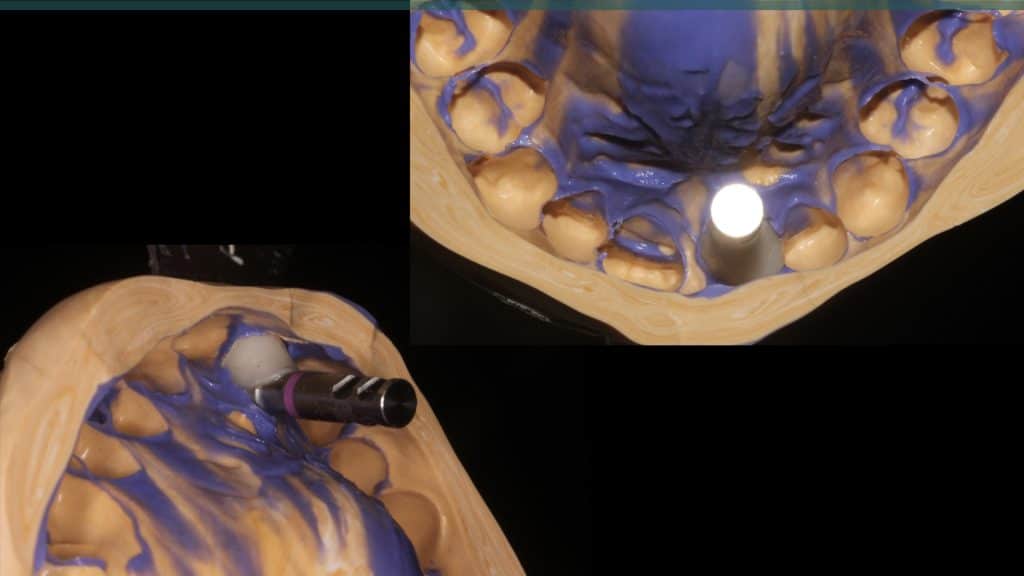
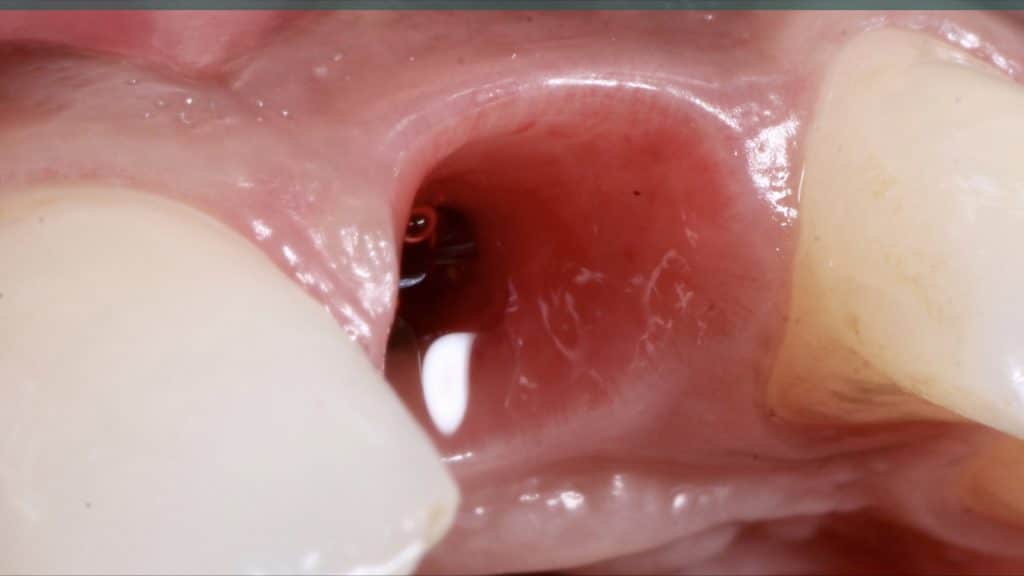
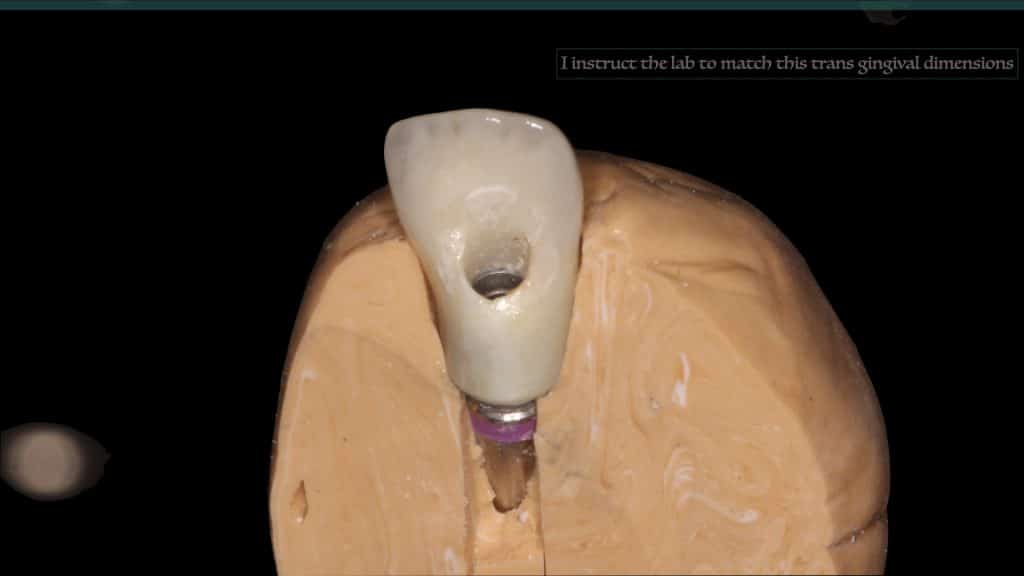
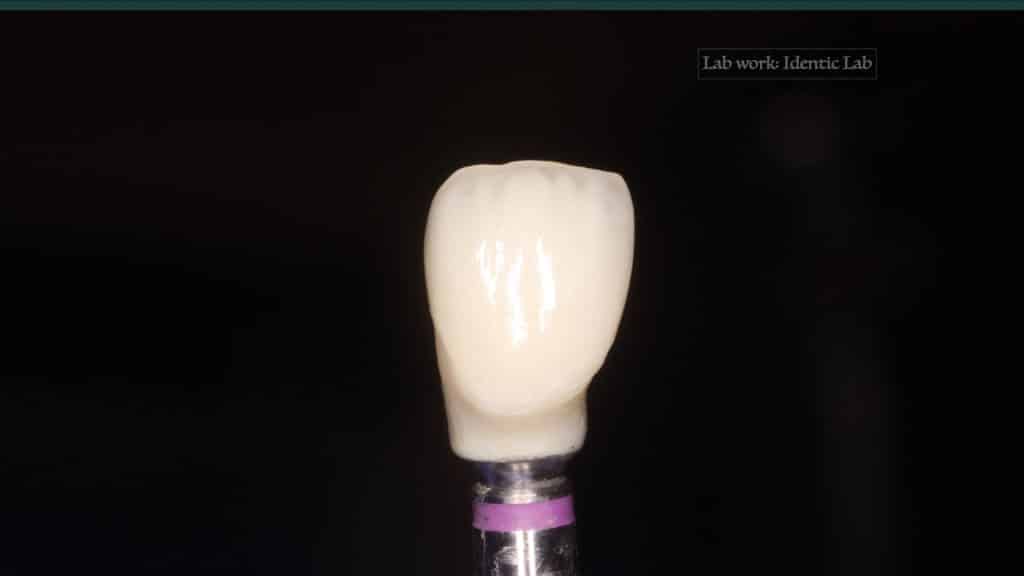
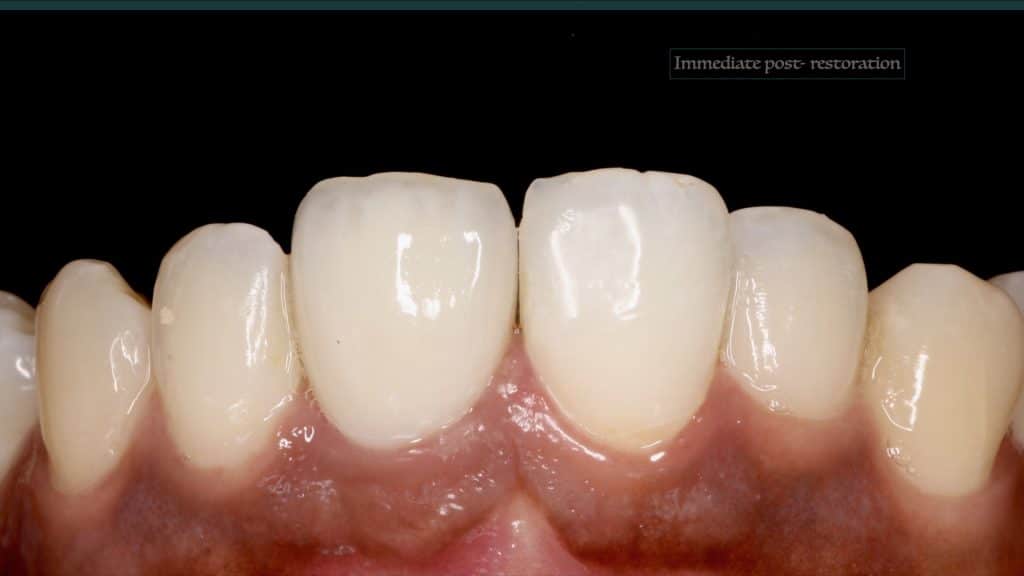
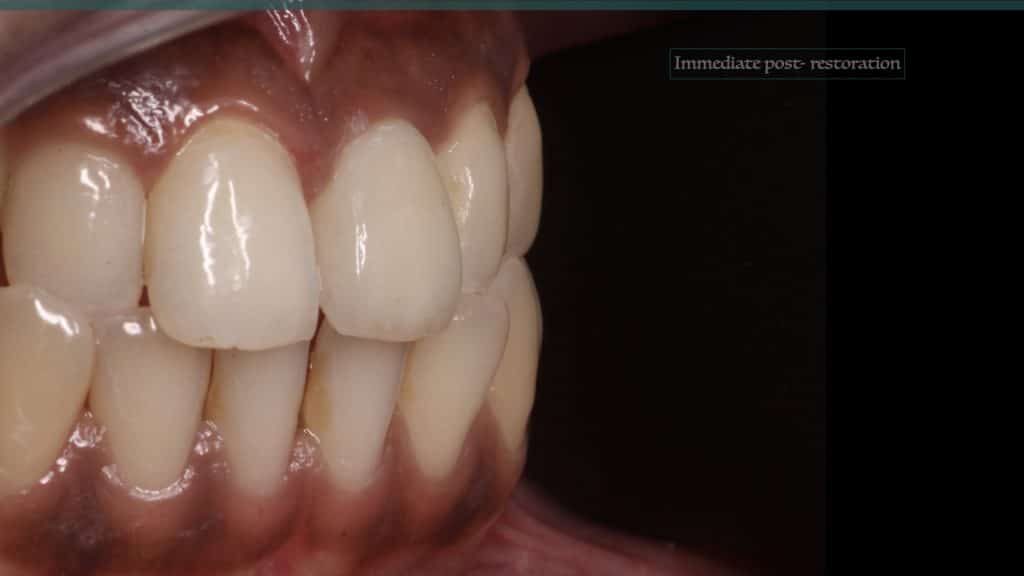
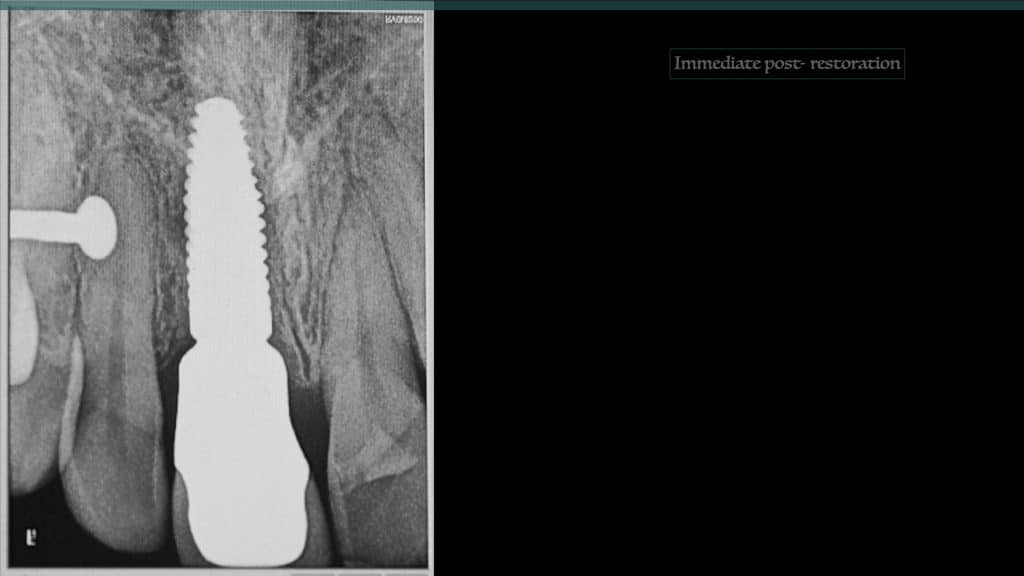
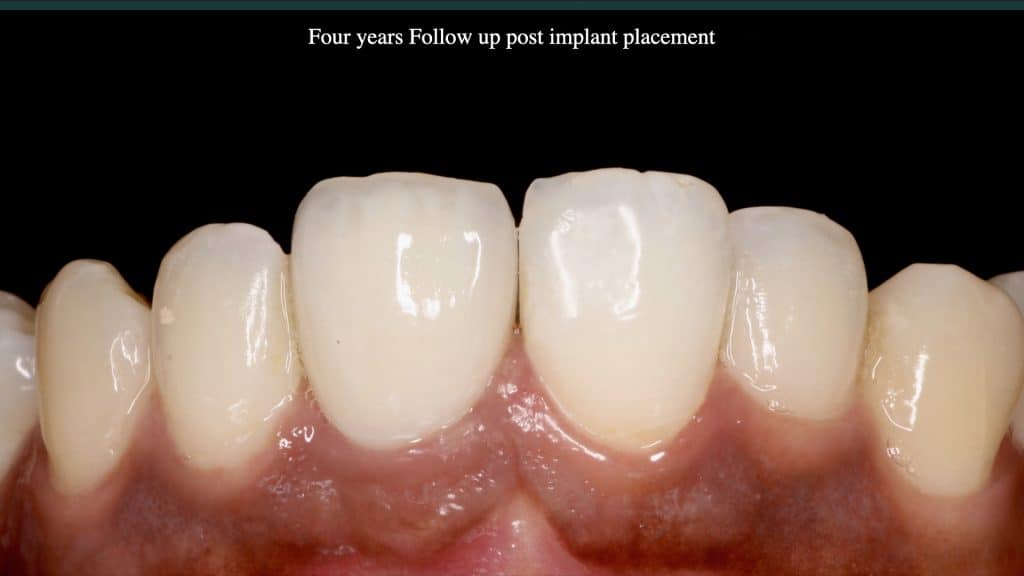
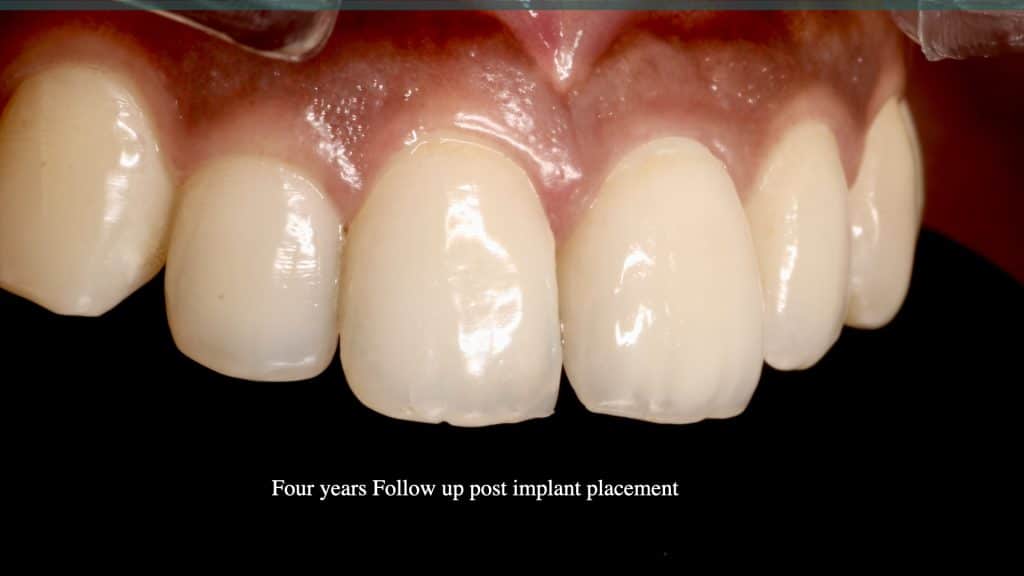
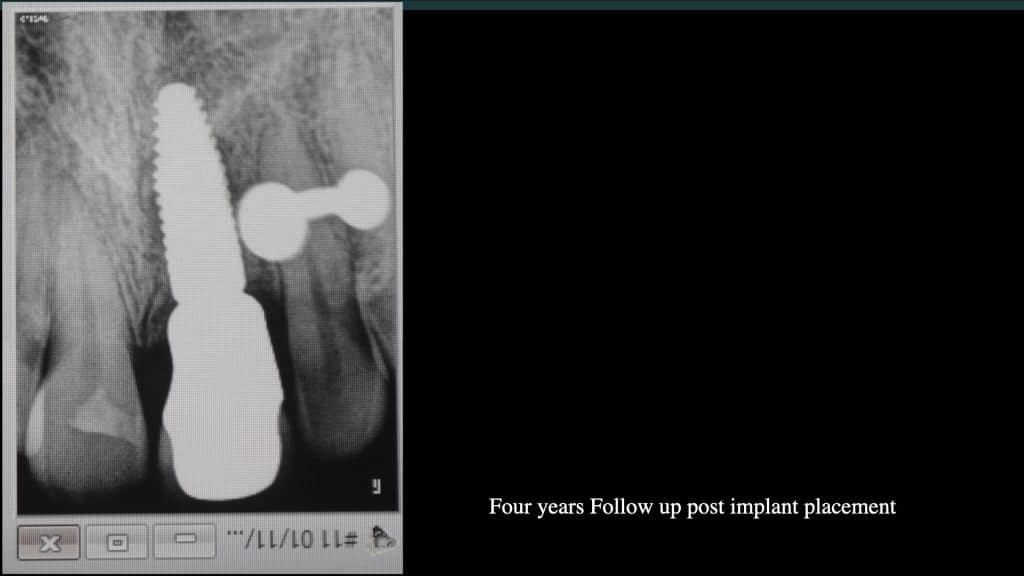
A 27-year female patient with dislodged Resin bonded FPD. She had that FPD for past few years, it had metal wings on palatal surfaces of UR1 and UL2 and a post like metal extension into the root canal of UL1. There was gingival abscess due to fractured root segment most probably due to extended metallic post like structure. Immediate implant placement (IIP) and Immediate restoration (IR) was planned for this patient.
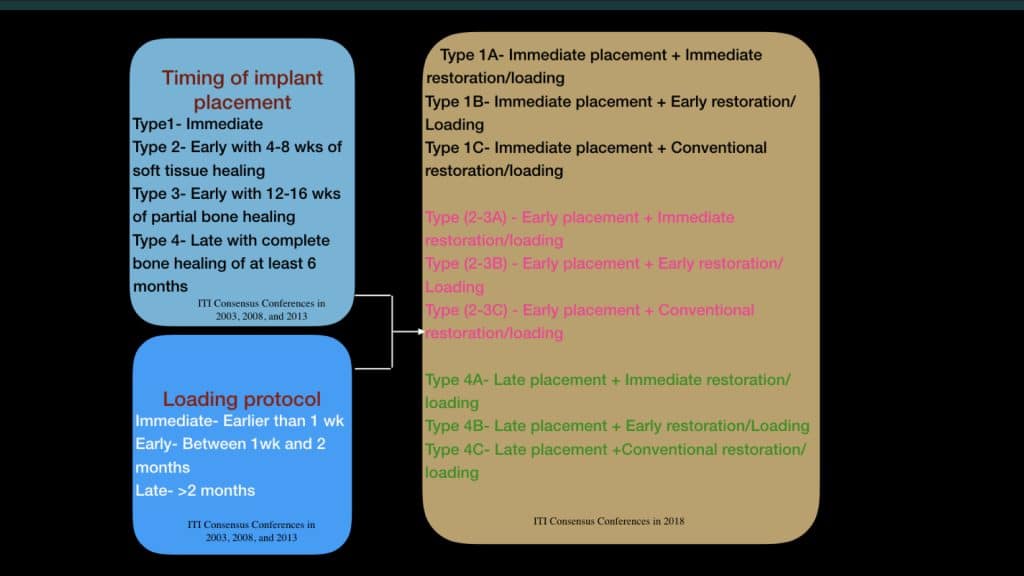
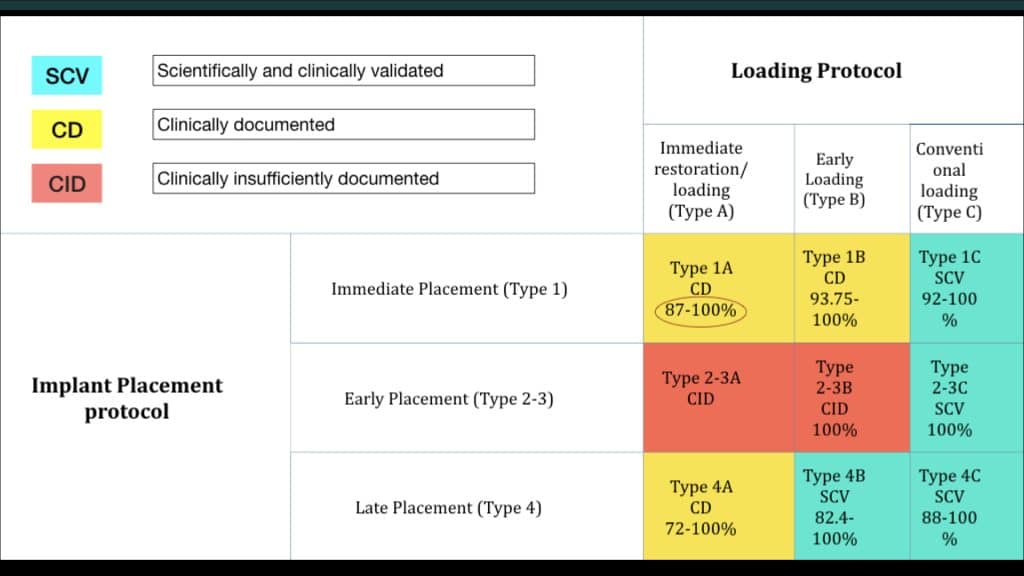
Galluci et al. reviewed the evidence for the clinical outcome of fixed implant prostheses treated with different combinations of implant placement and loading protocols in partially edentulous patients.
They formulated conclusions and proposed clinical recommendations for all types of placement and loading protocols; the included studies were ranked per their design, sample size, and outcome homogeneity (OH). The outcome homogeneity was considered positive (OH+) when the variation of implant survival rates for the same treatment protocol was 10% or less, and negative (OH–) when the variation was >10% (Gallucci et al., 2009).
Type 1A was deemed according the validation tool as presenting clinical documentation. Although there were six comparative studies and 18 noncomparative studies in this group, the validation of this protocol was influenced by a negative outcome homogeneity (OH) ranging from 87.5% to 100% survival rate. The studies that reported on the success criteria showed a range of 87% to 100%. From the studies assessing Type 1A, carefully case selection criteria were described. Here, the presence of sufficient apical bone, intact buccal plate, and absence of infection at the extraction site was predominant. For Type 1A, the negative OH should be considered as clinical relevant particularly when careful patient selection criteria are recommended.
Implant placement and loading protocols in partially edentulous patients: A systematic review
German O. Gallucci1 | Adam Hamilton2 | Wenjie Zhou3,4 | Daniel Buser5 | Stephen Chen6
Clin Oral Impl Res. 2018;29(Suppl. 16):106–134.
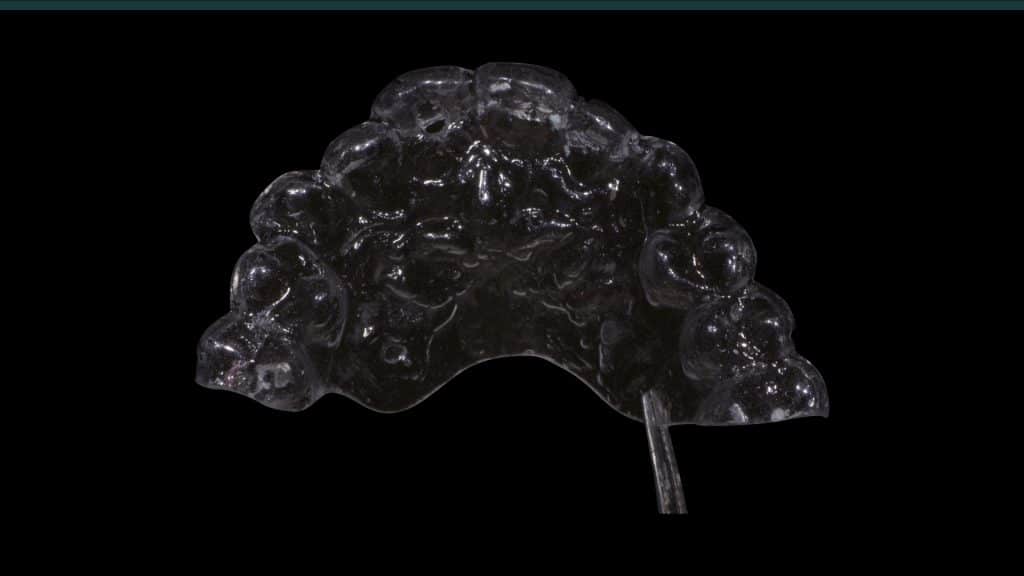
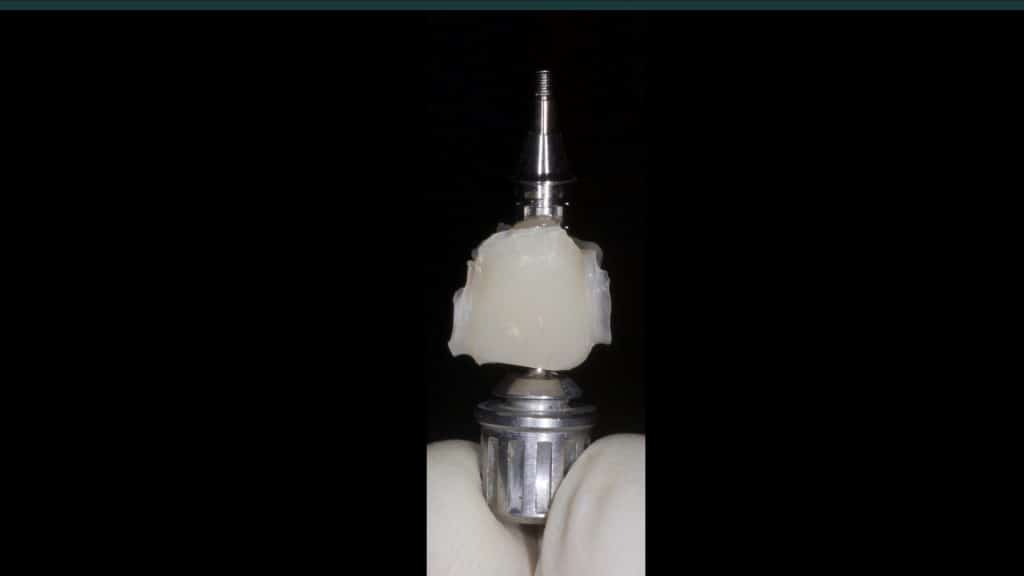
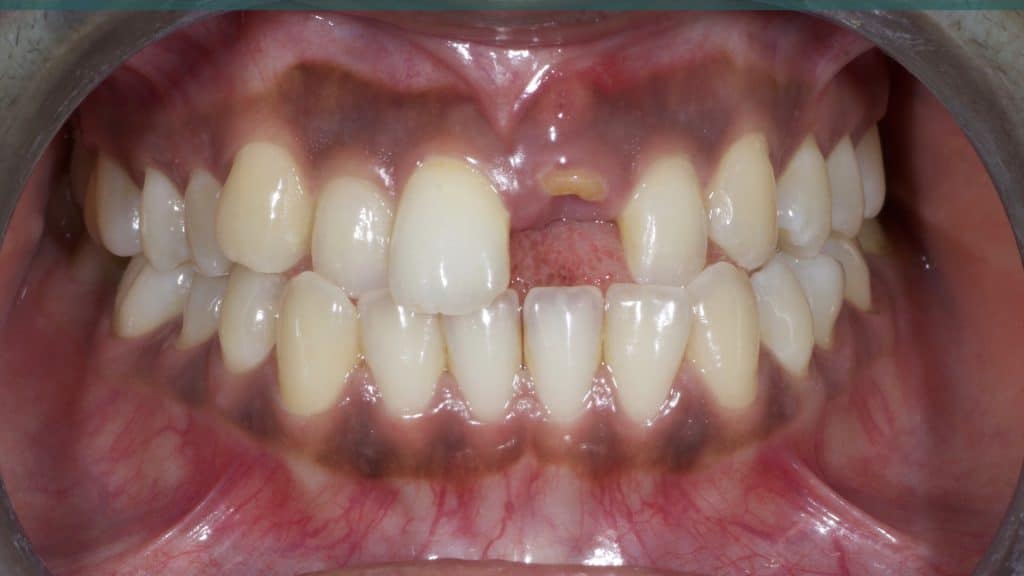
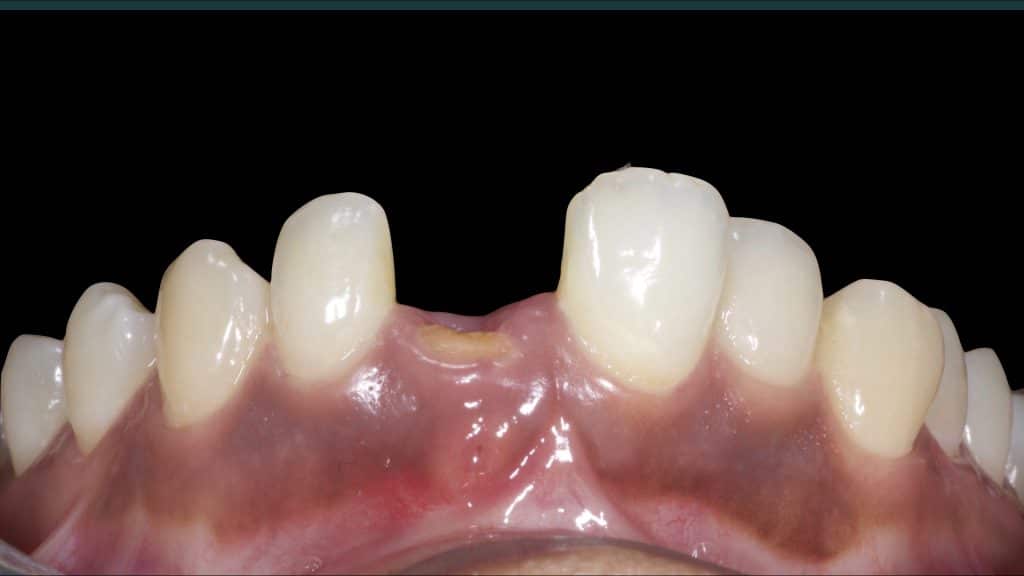
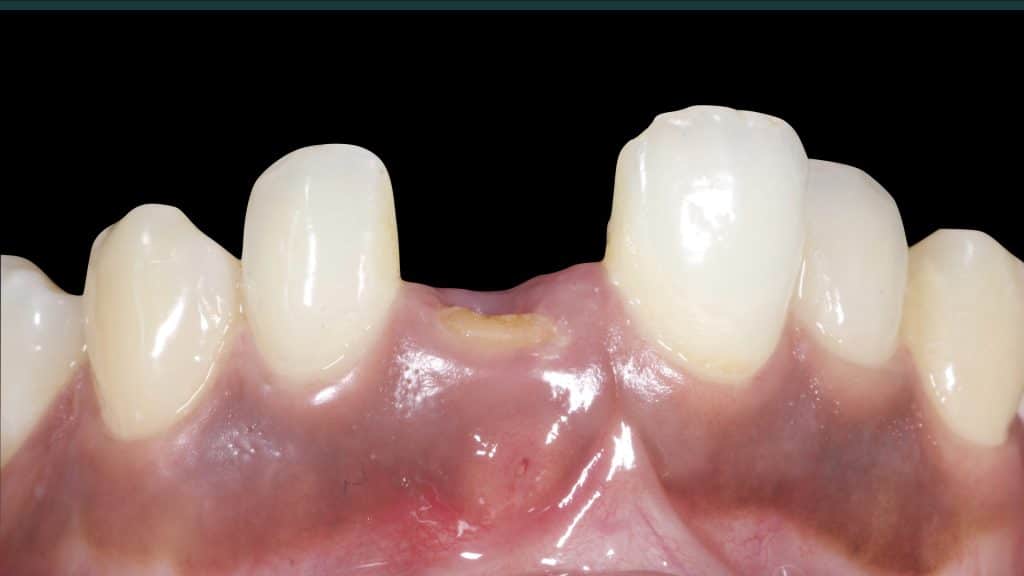
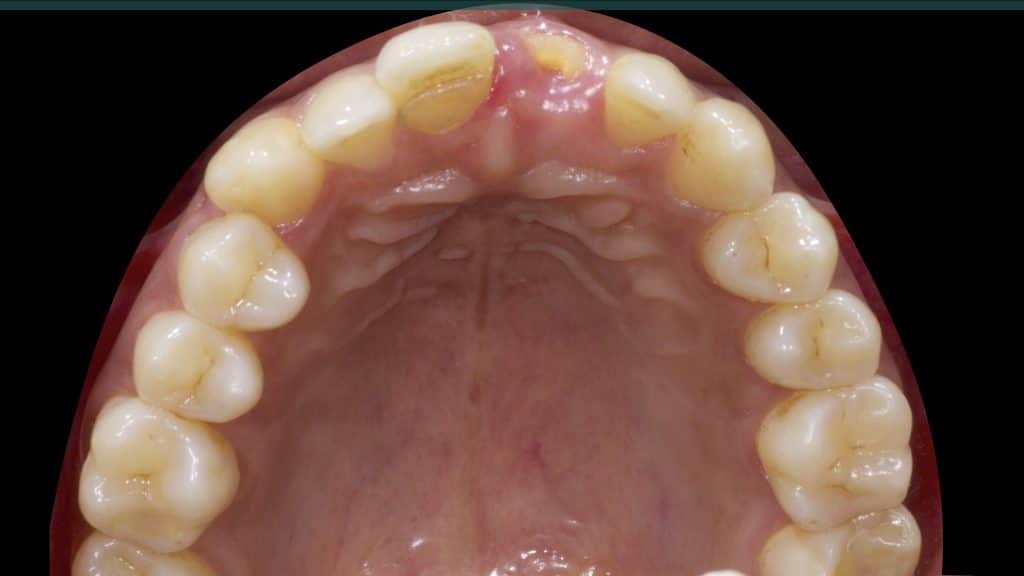
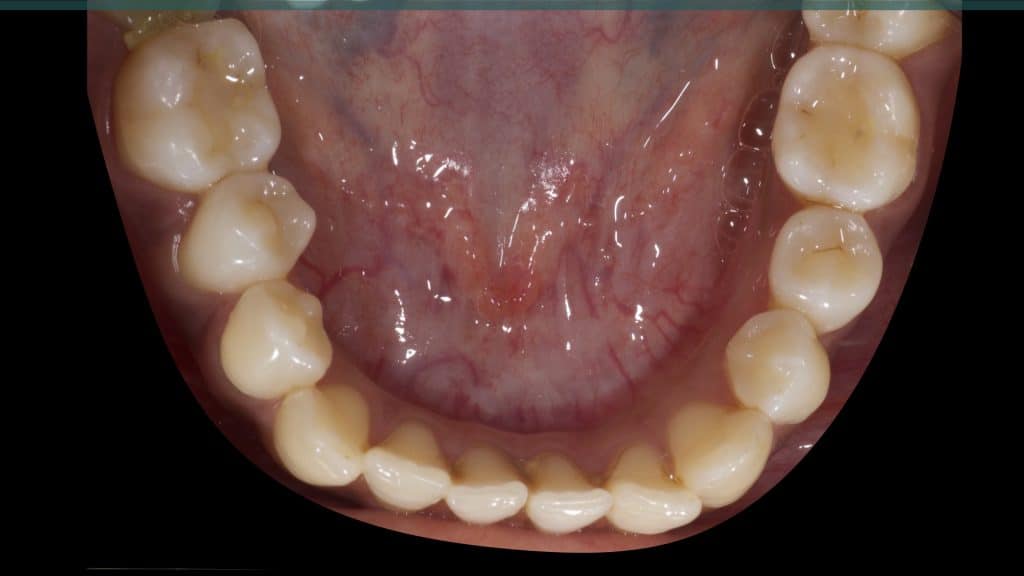
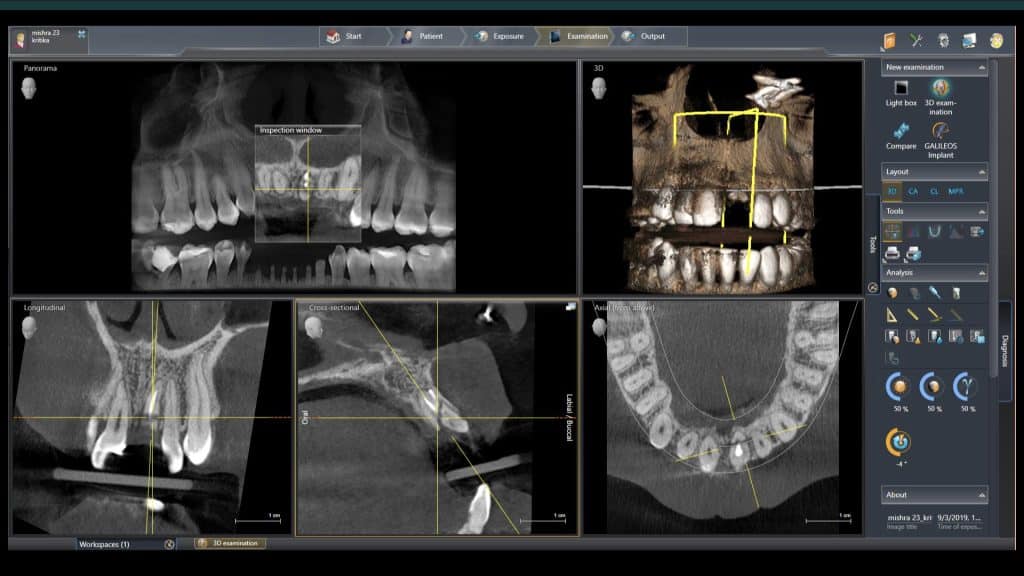
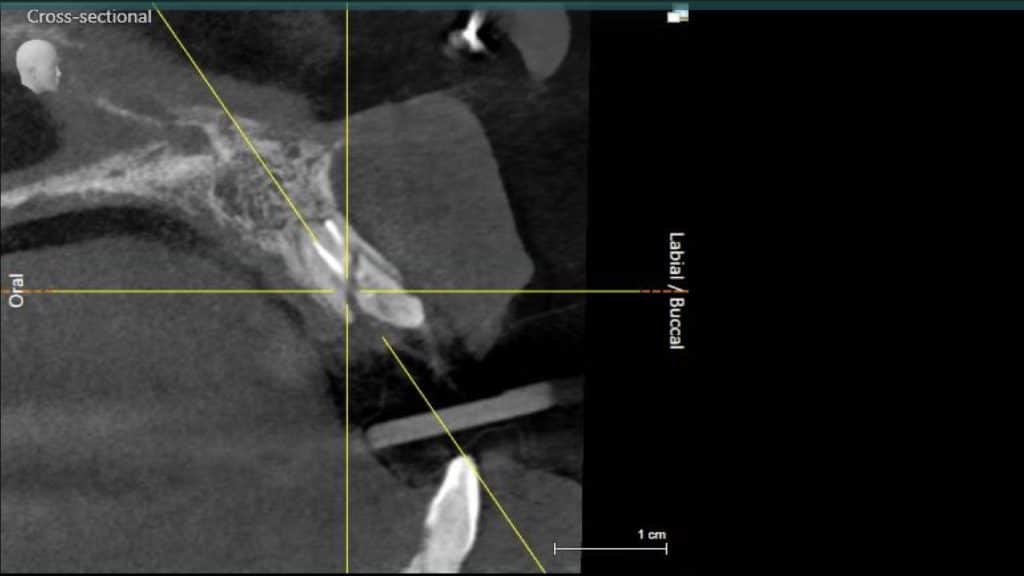

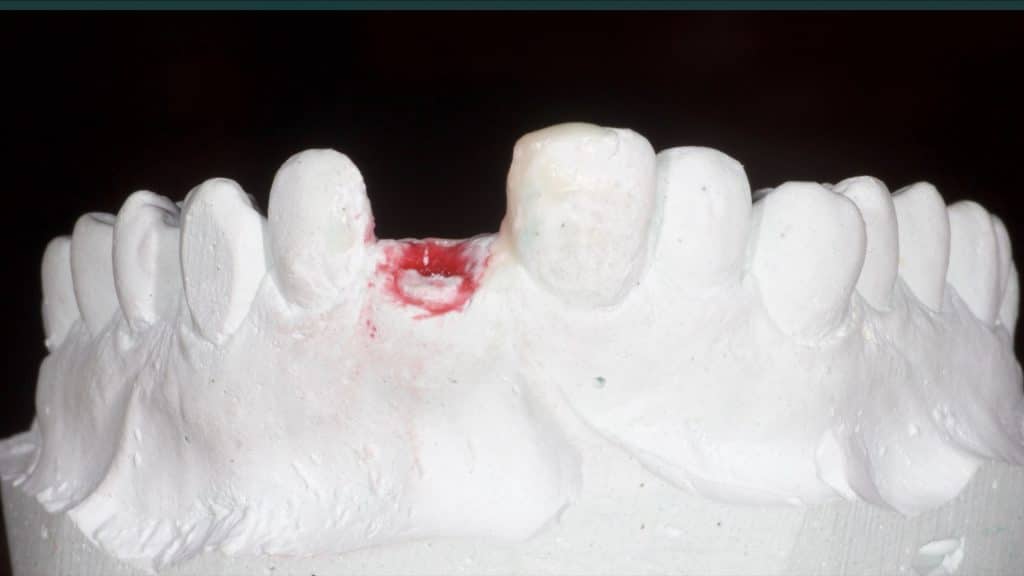
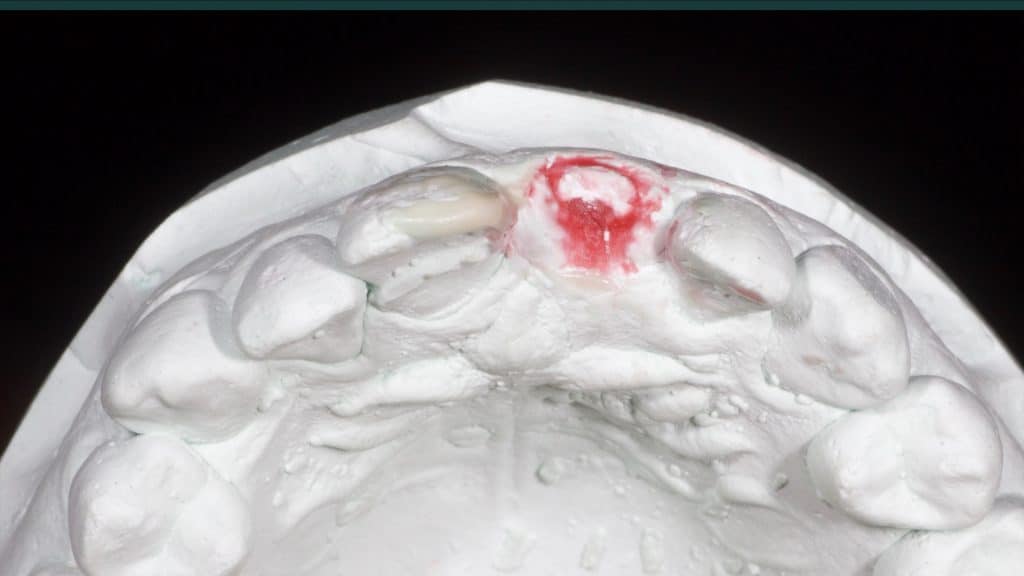
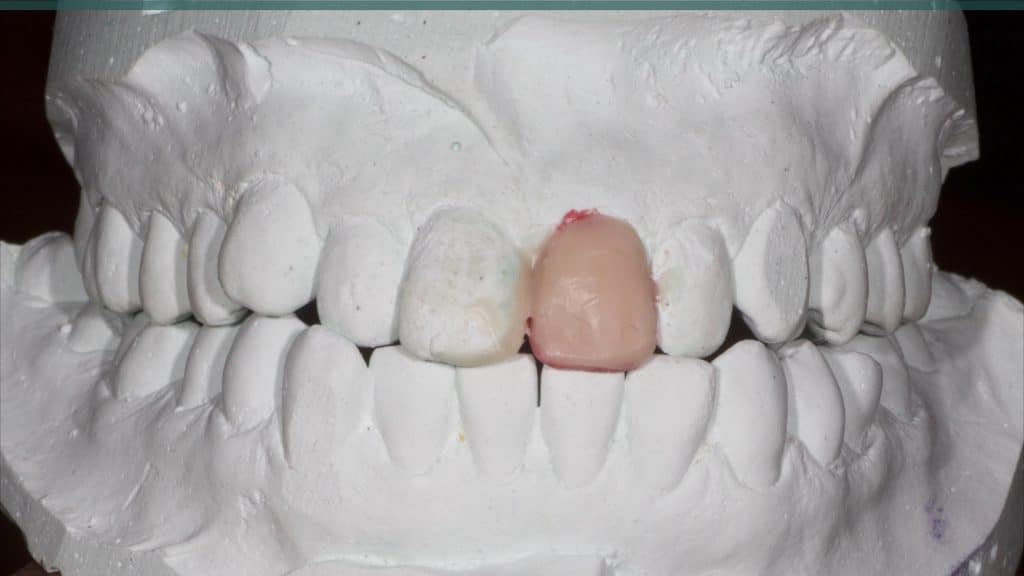
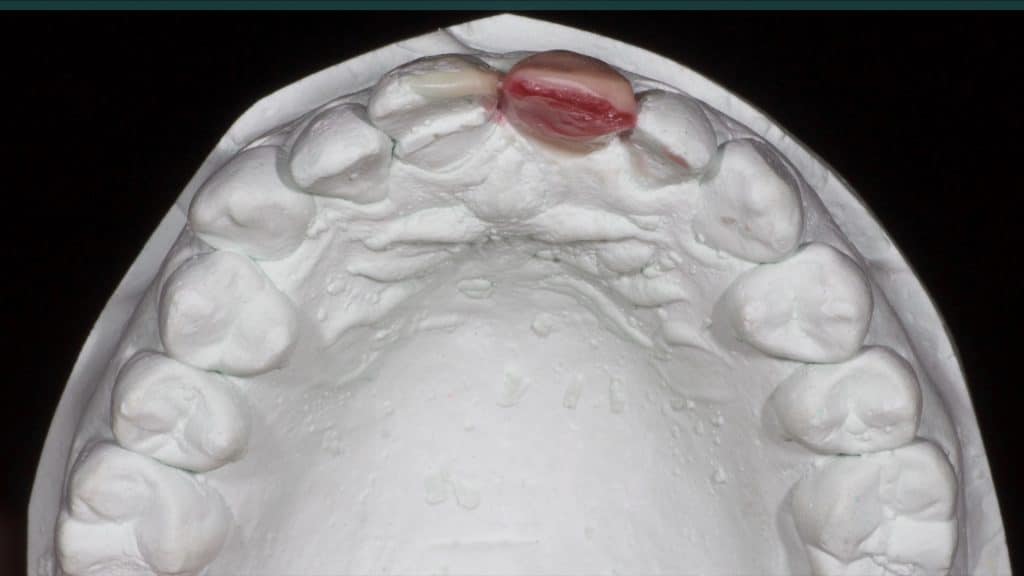
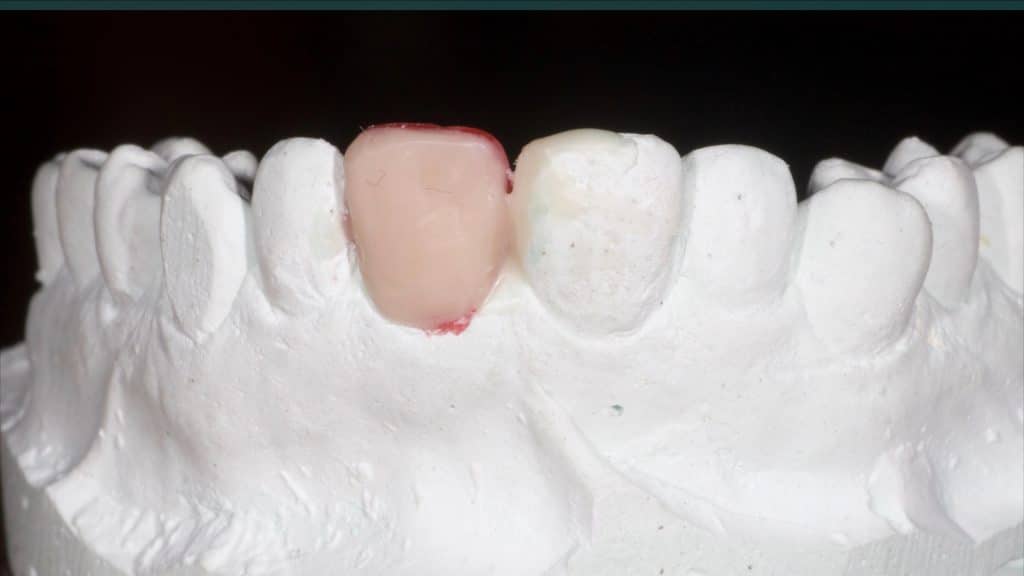
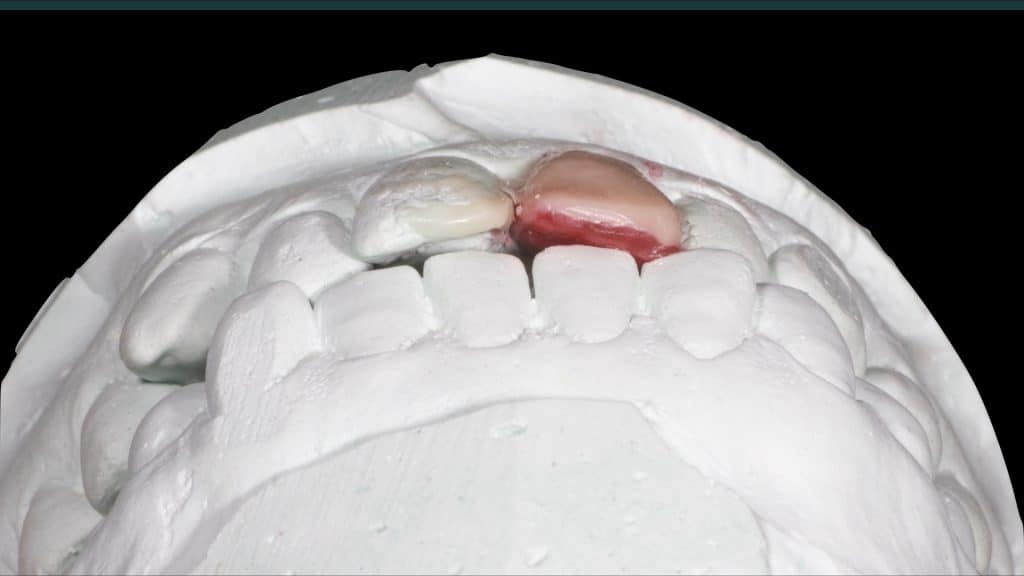

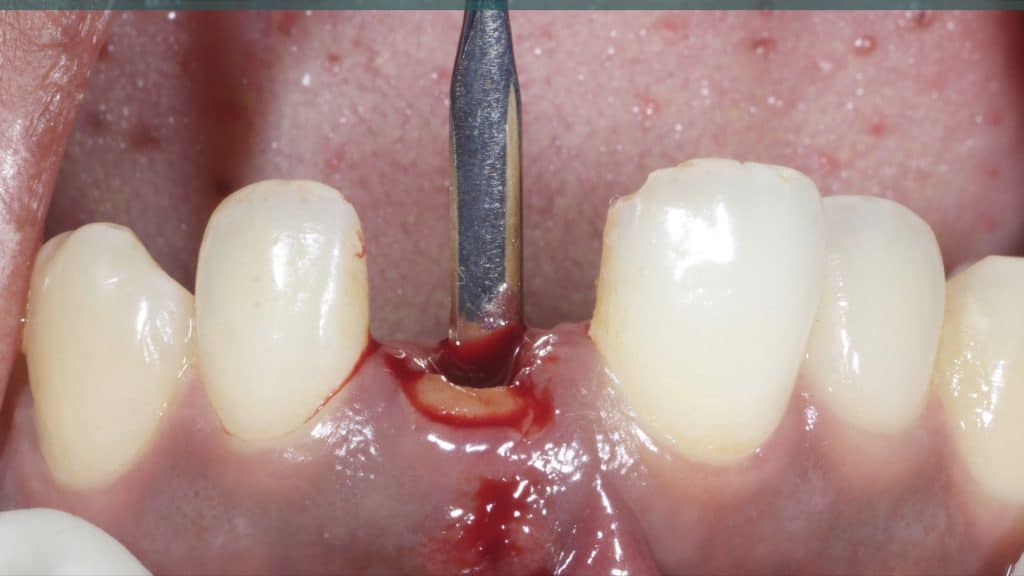
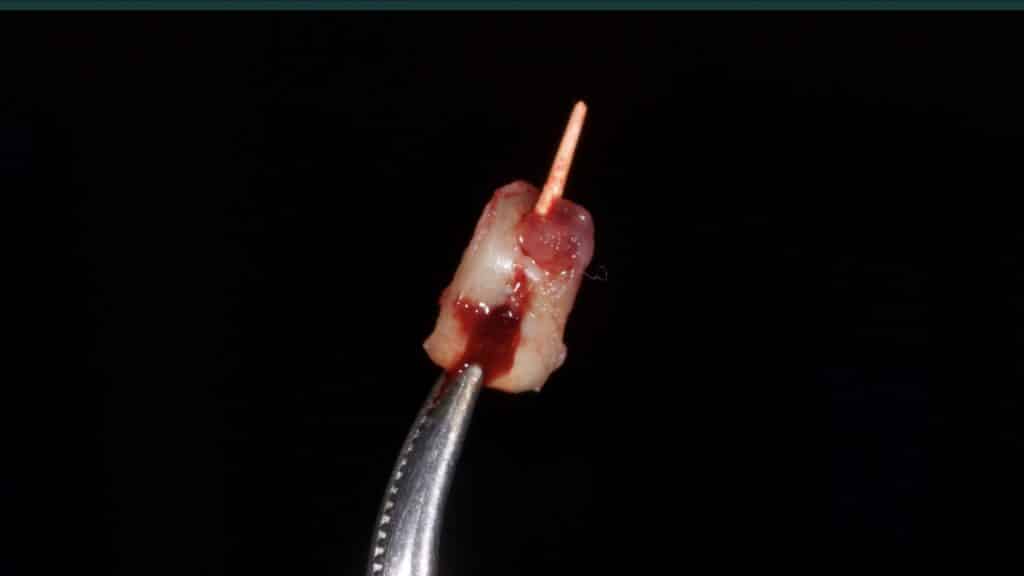
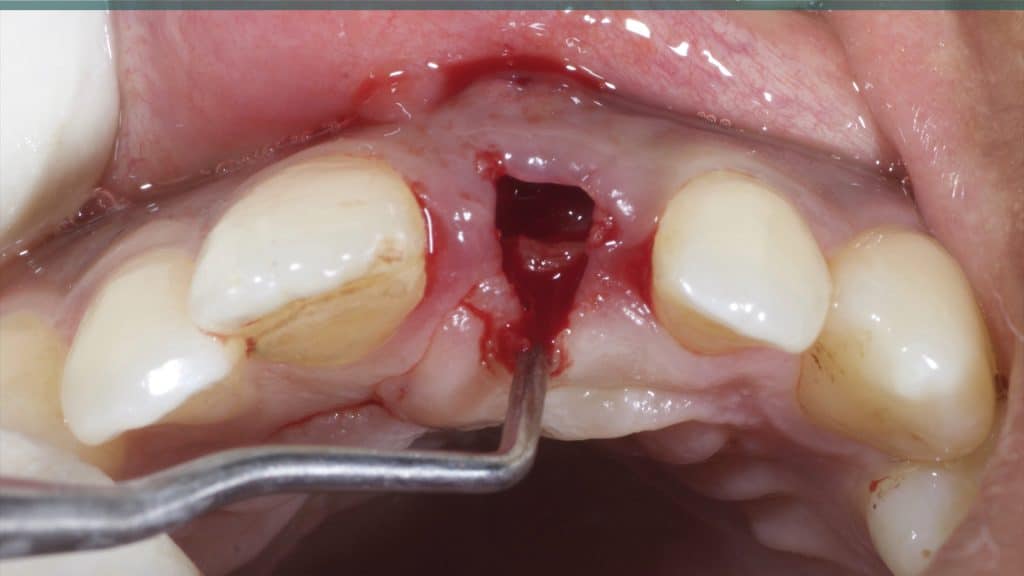

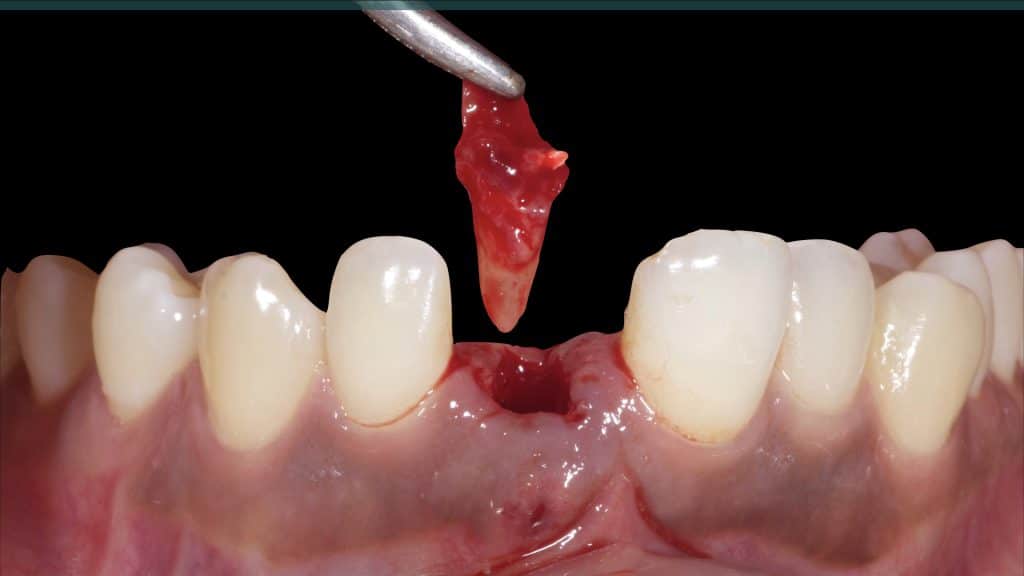
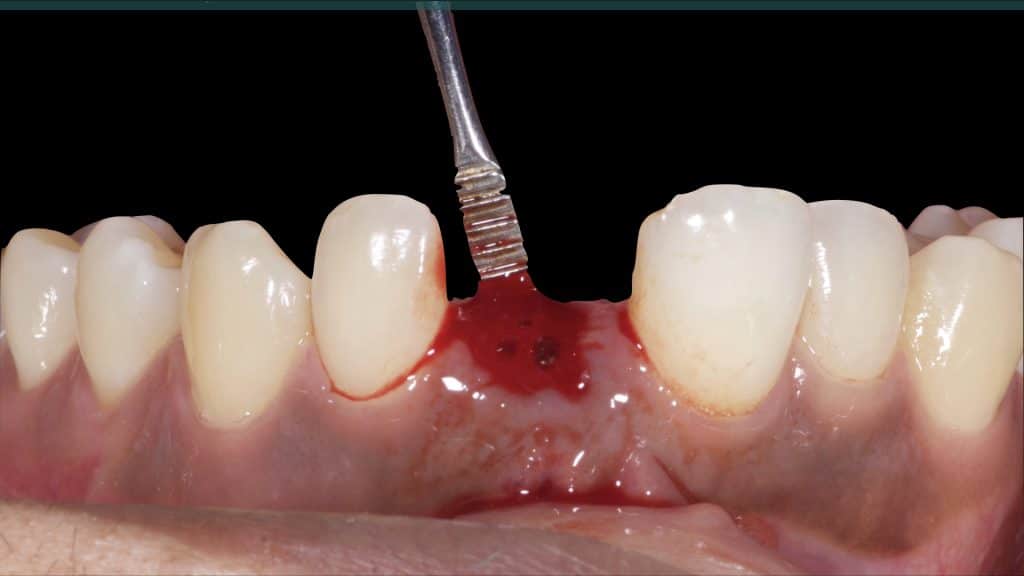
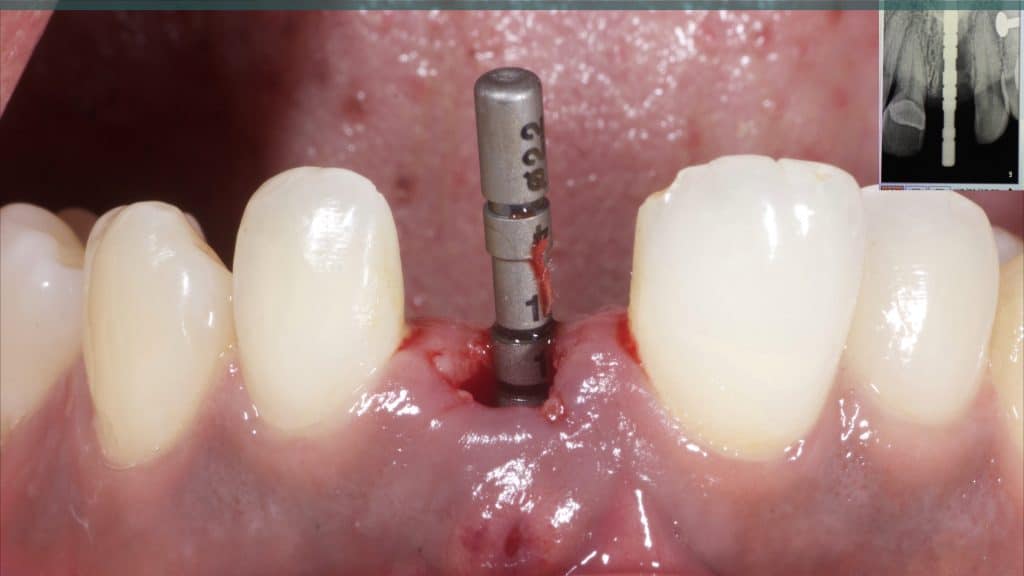
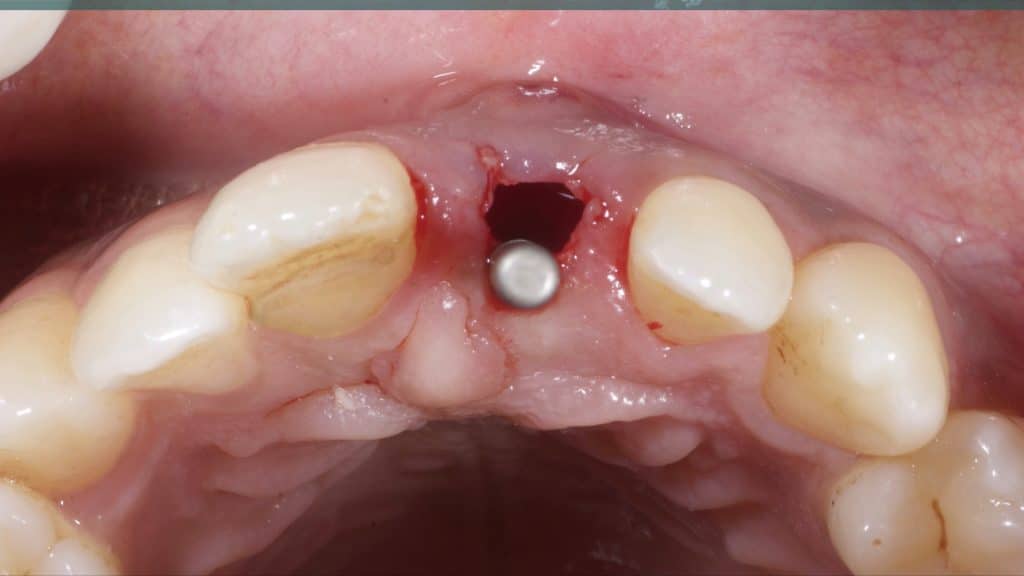
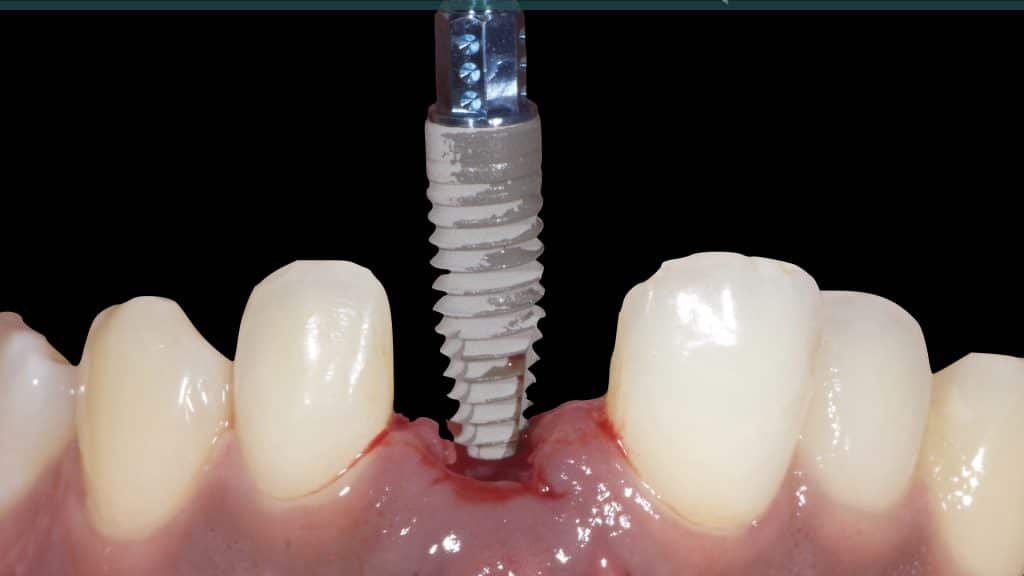
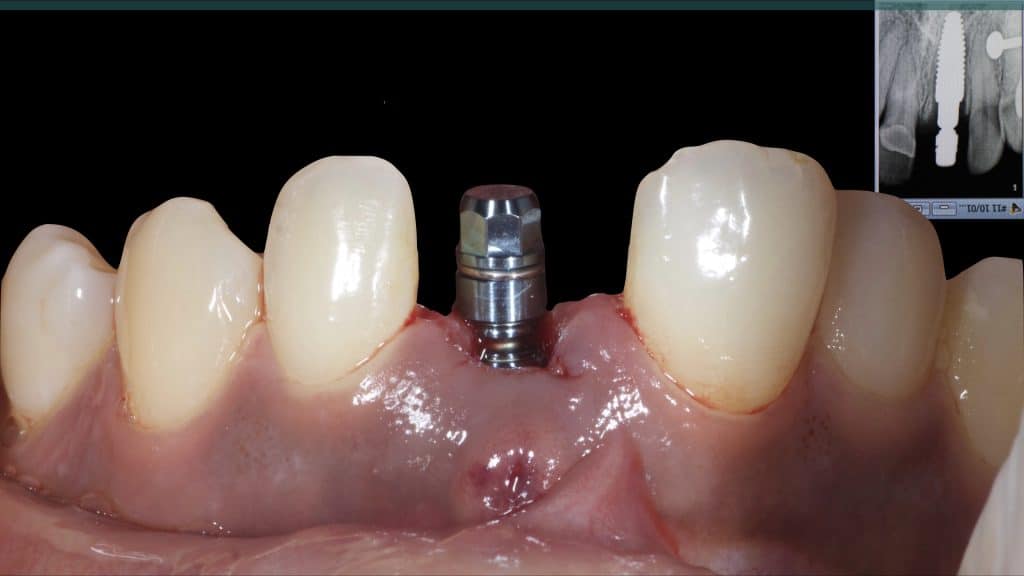

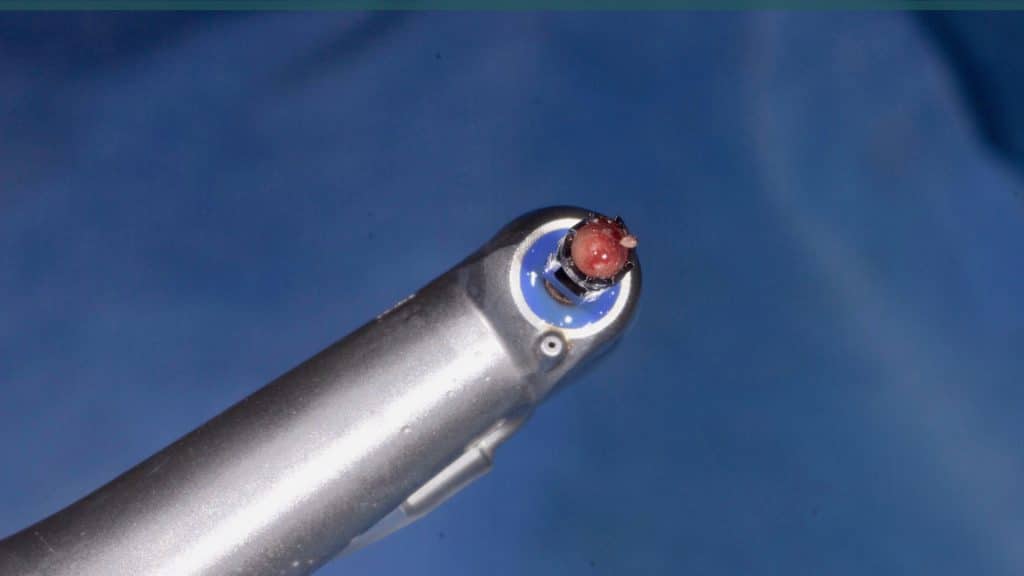
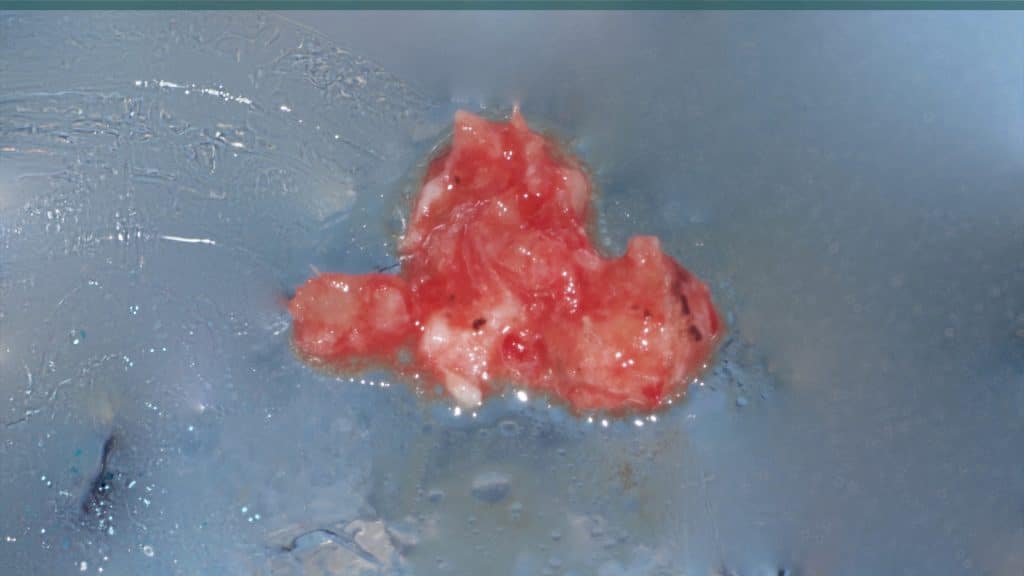
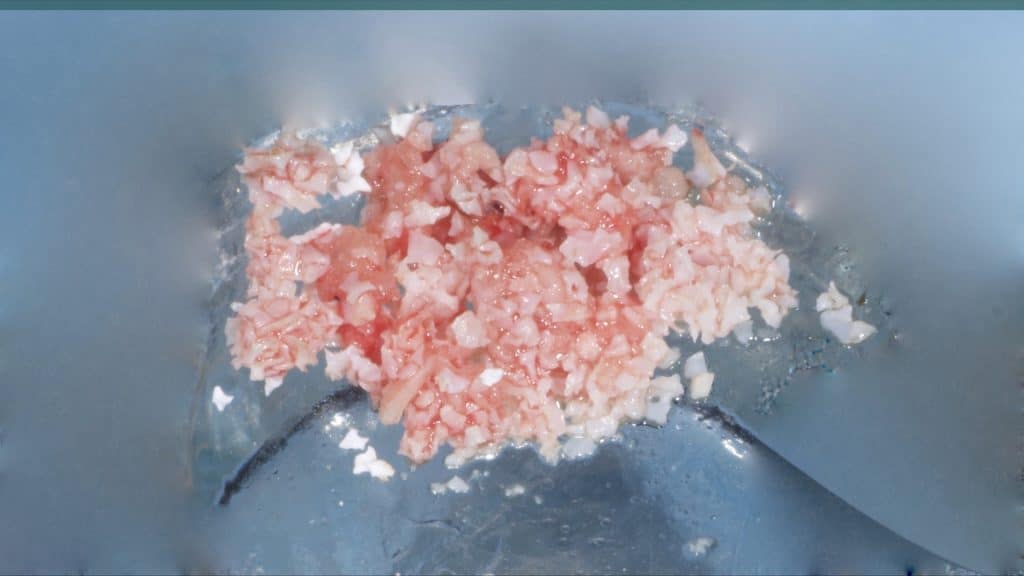
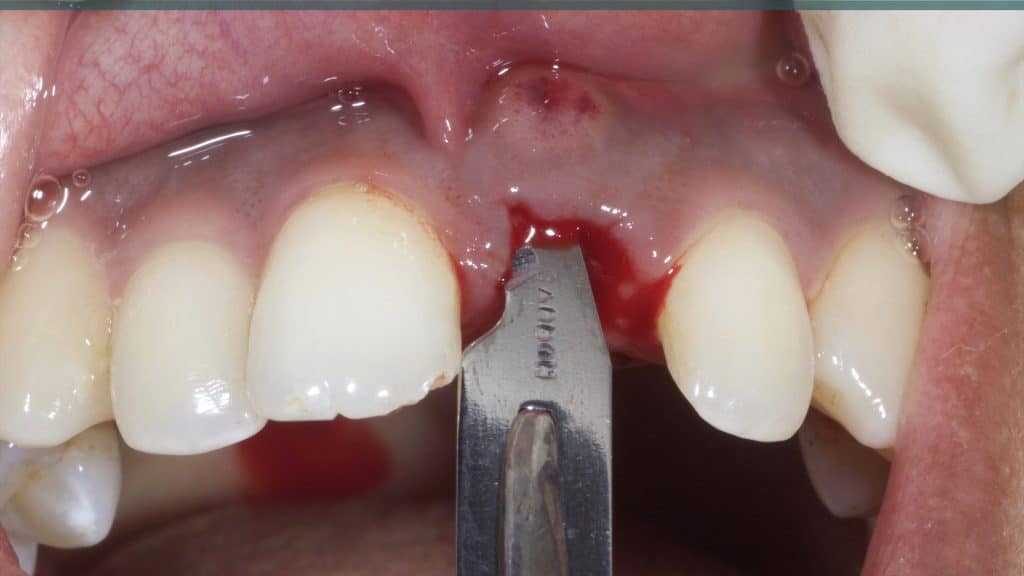
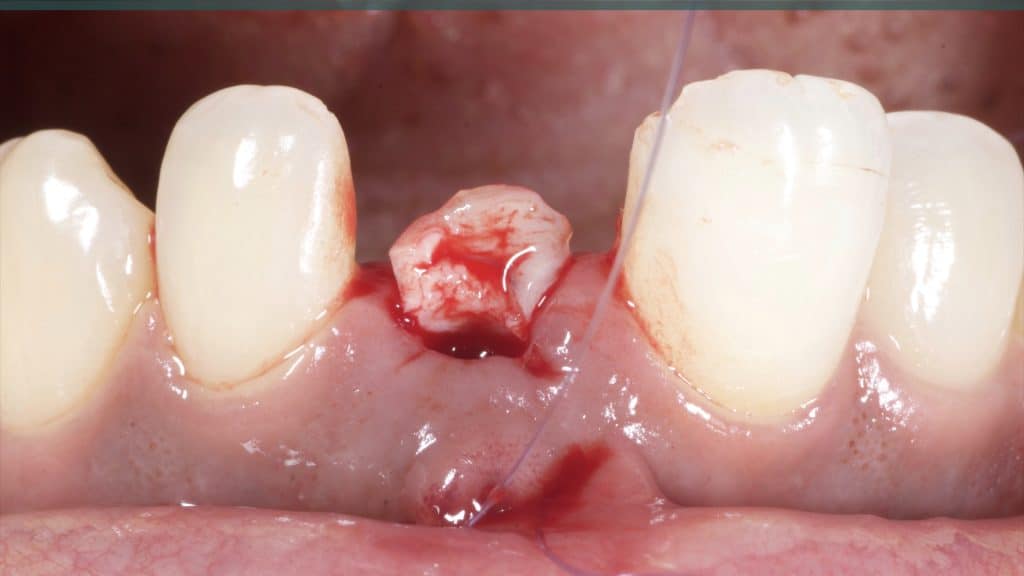




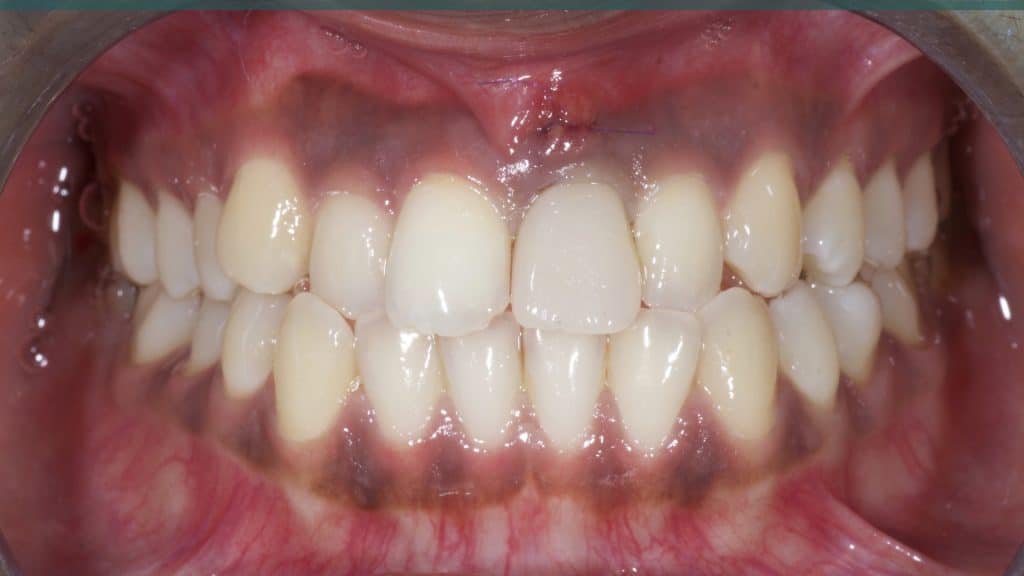
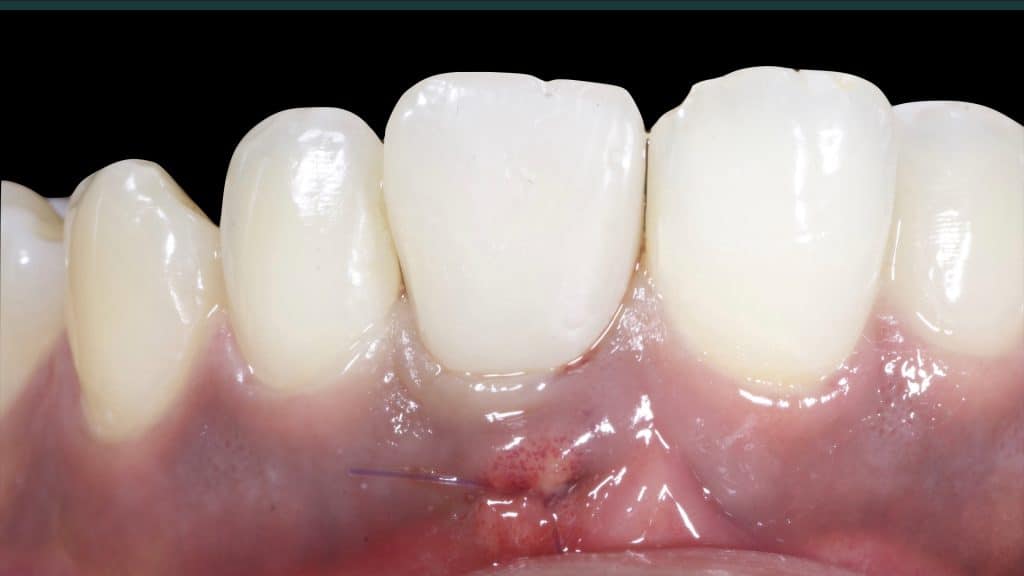
Immediate post-op
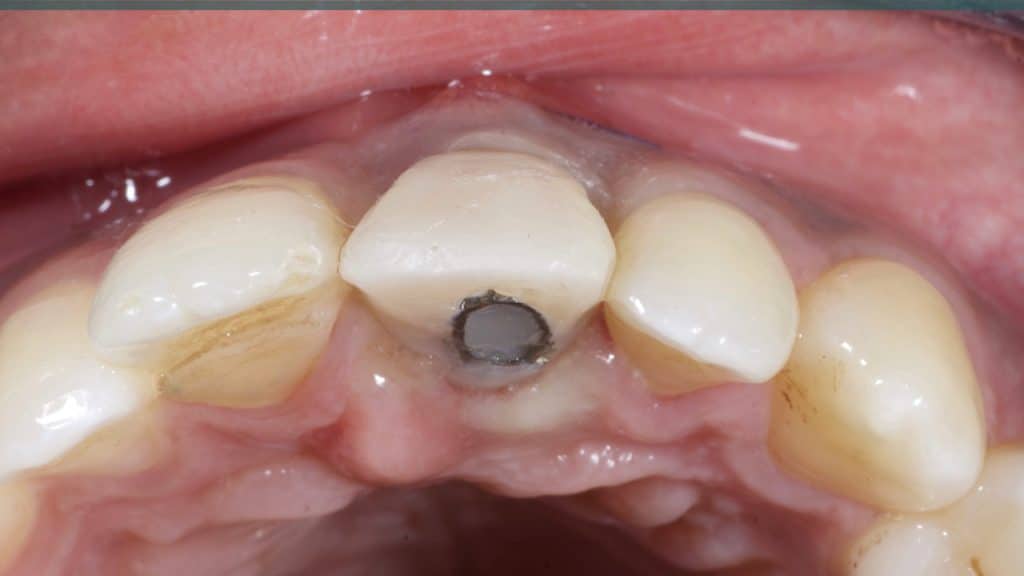
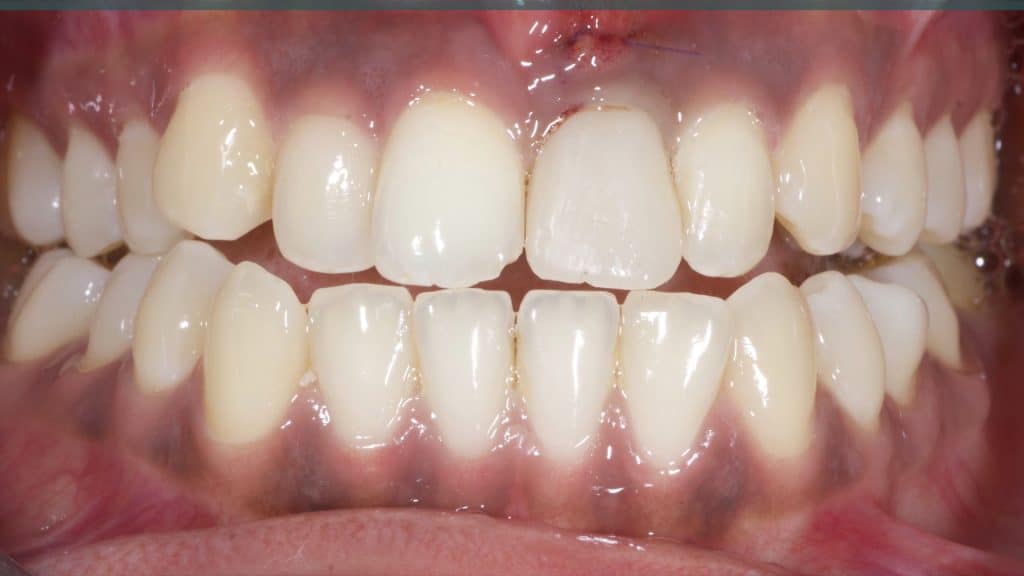
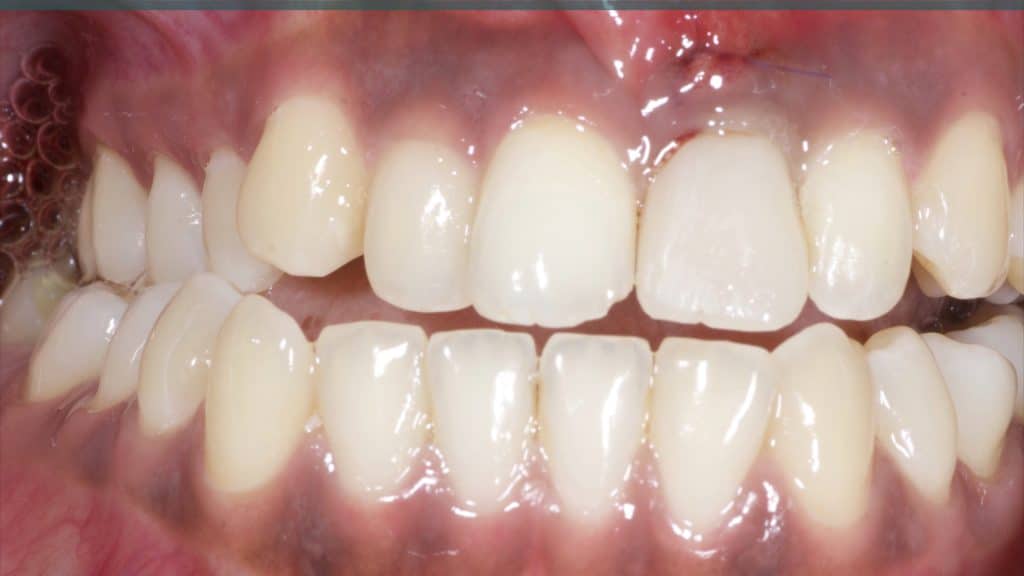
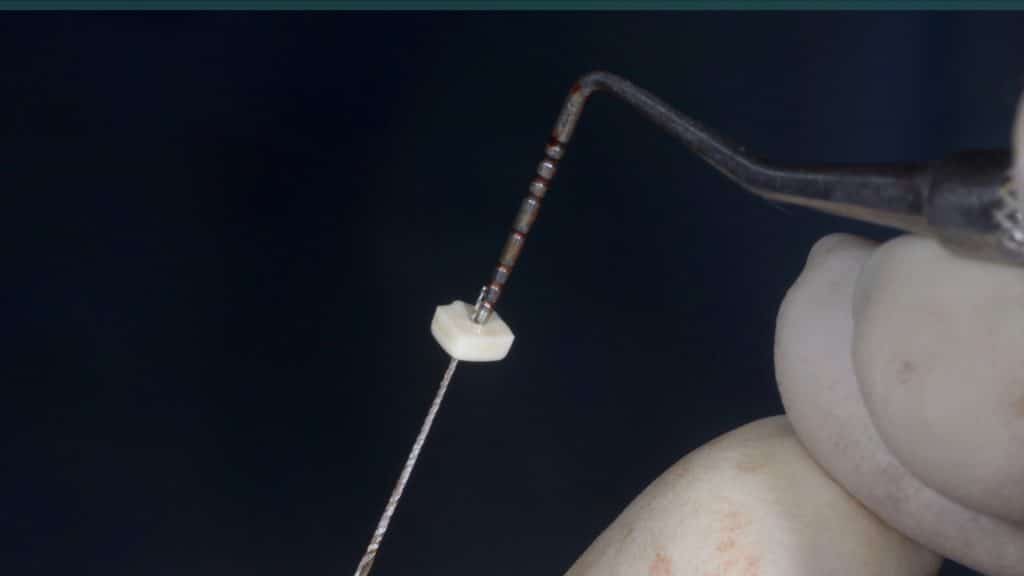
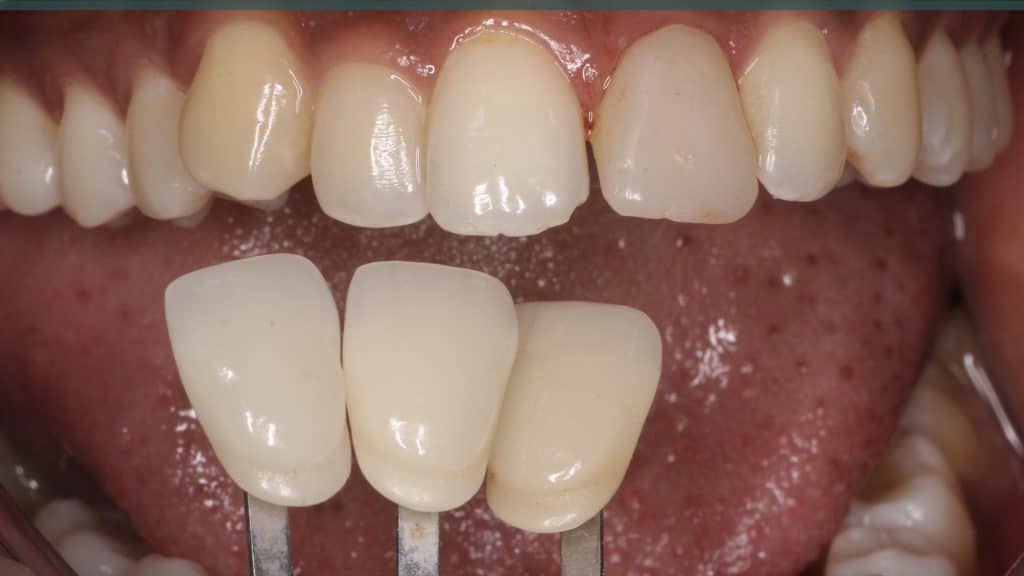
Occlusal check
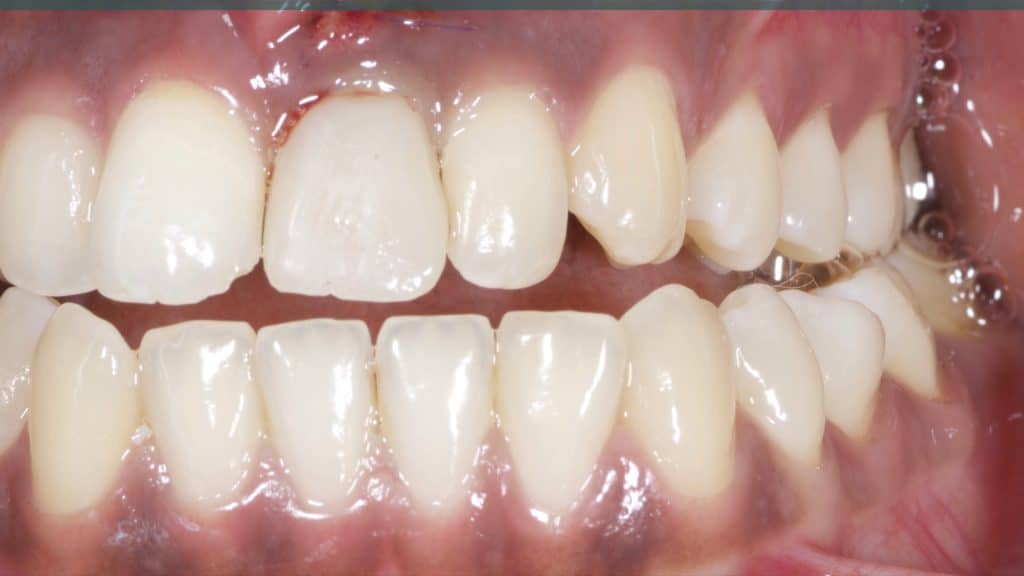
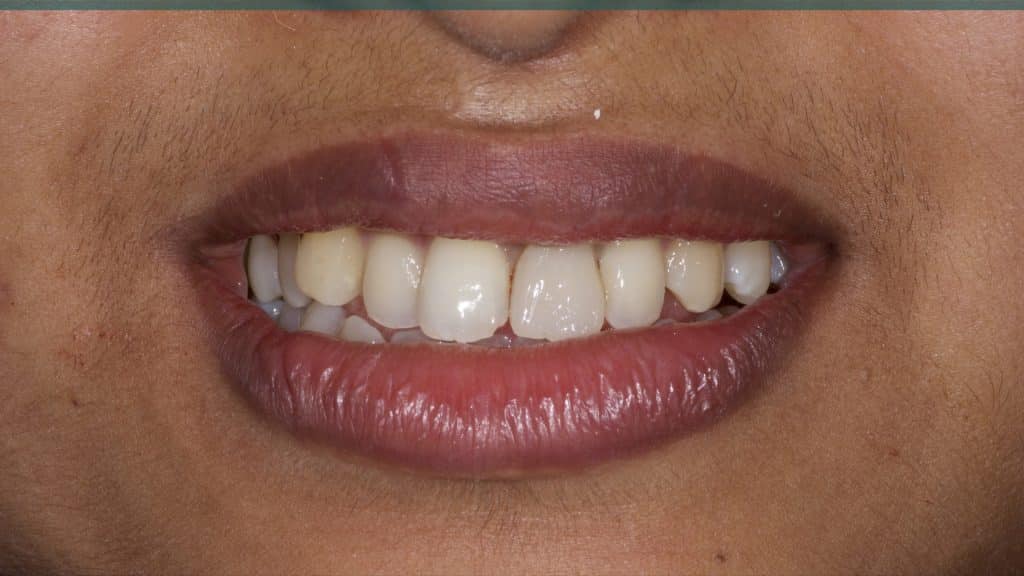
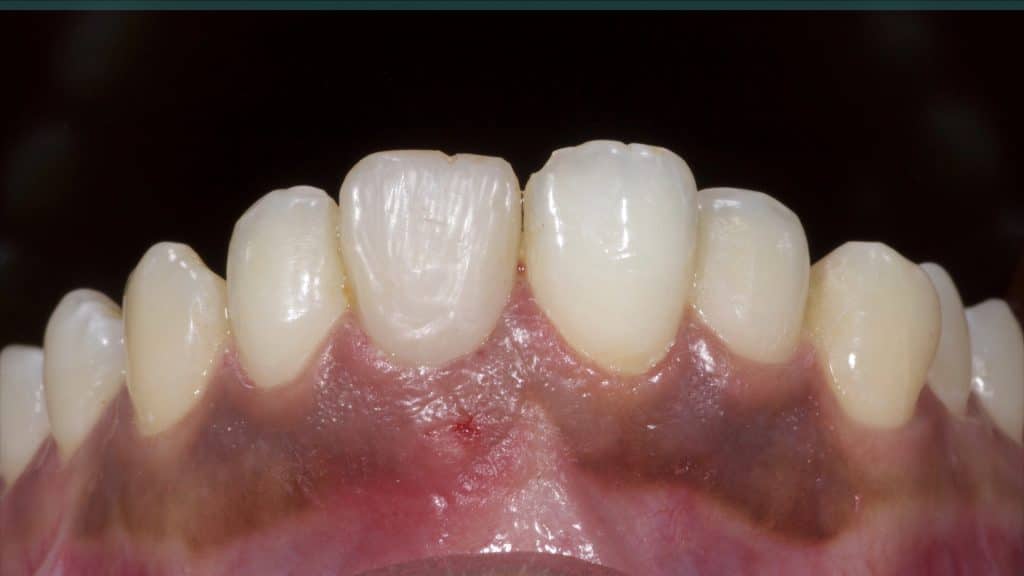
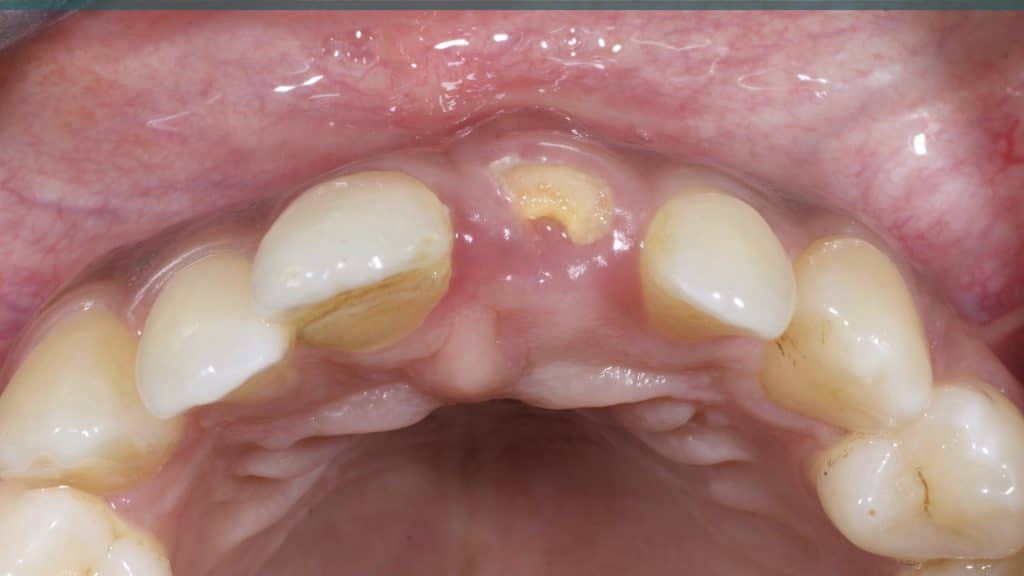
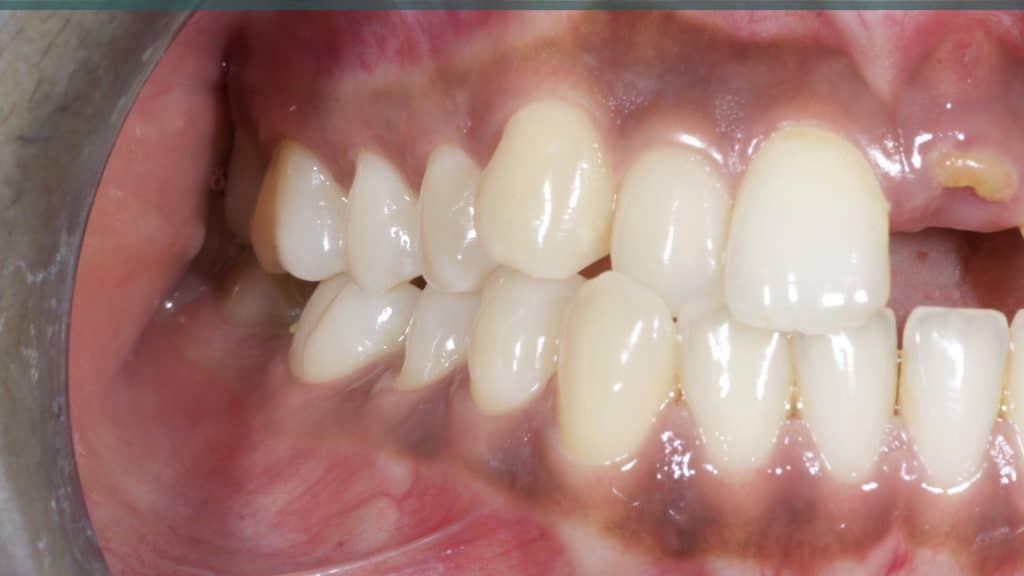
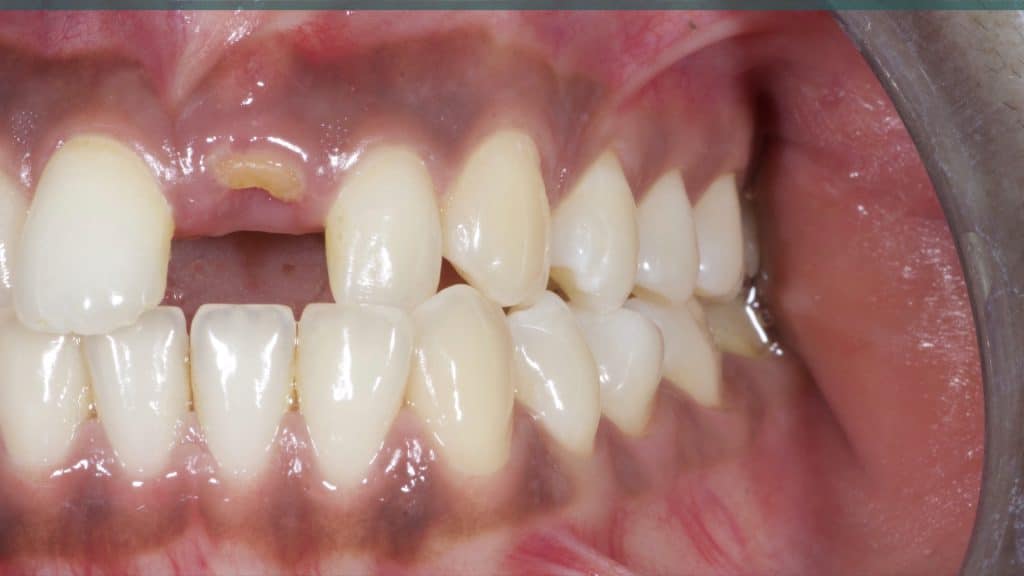
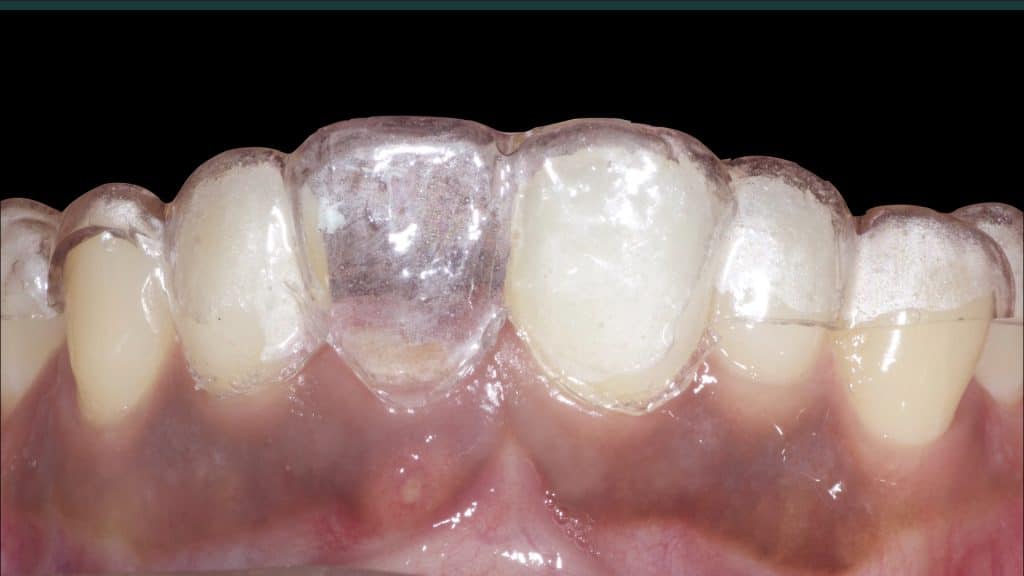
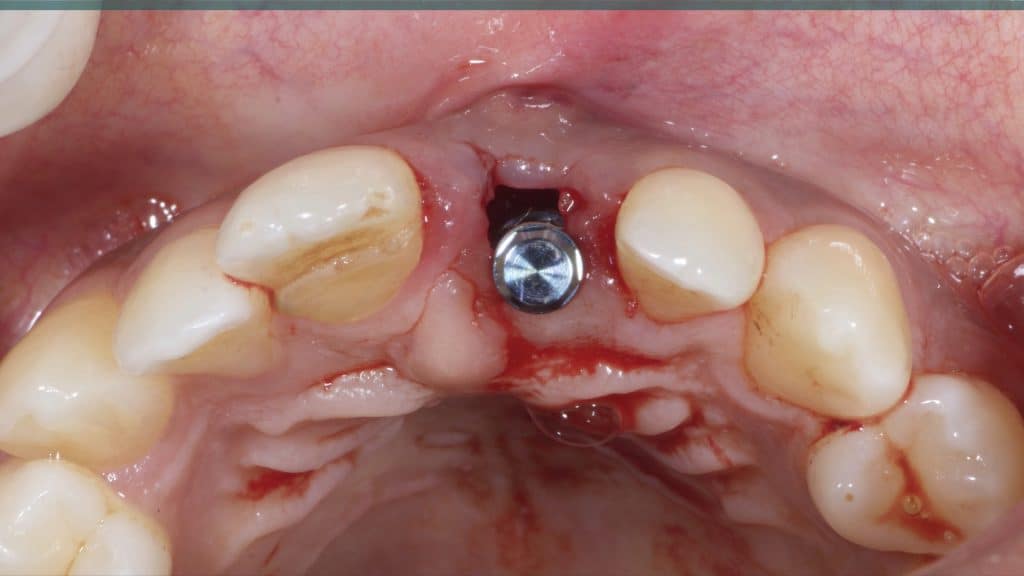
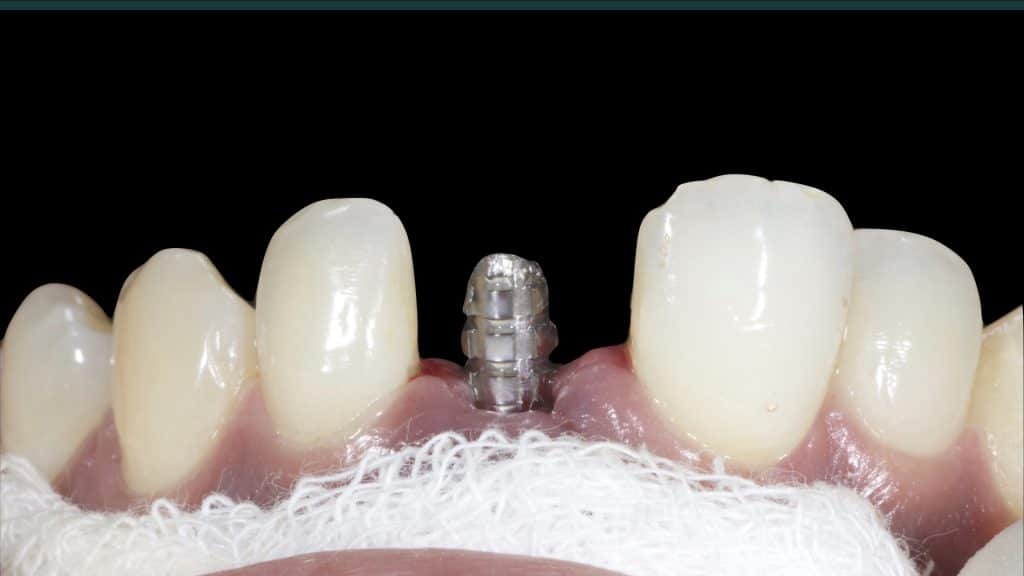
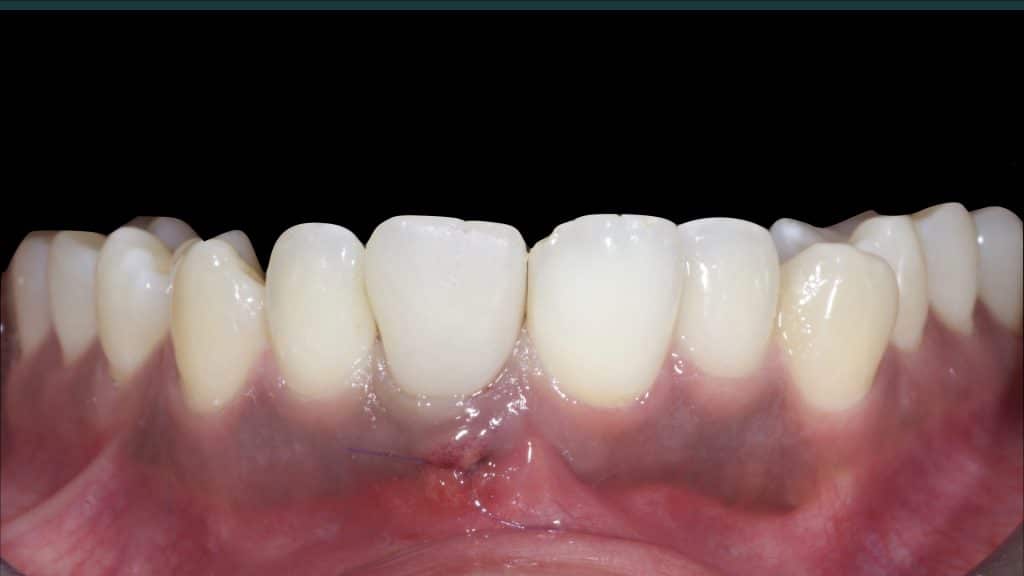
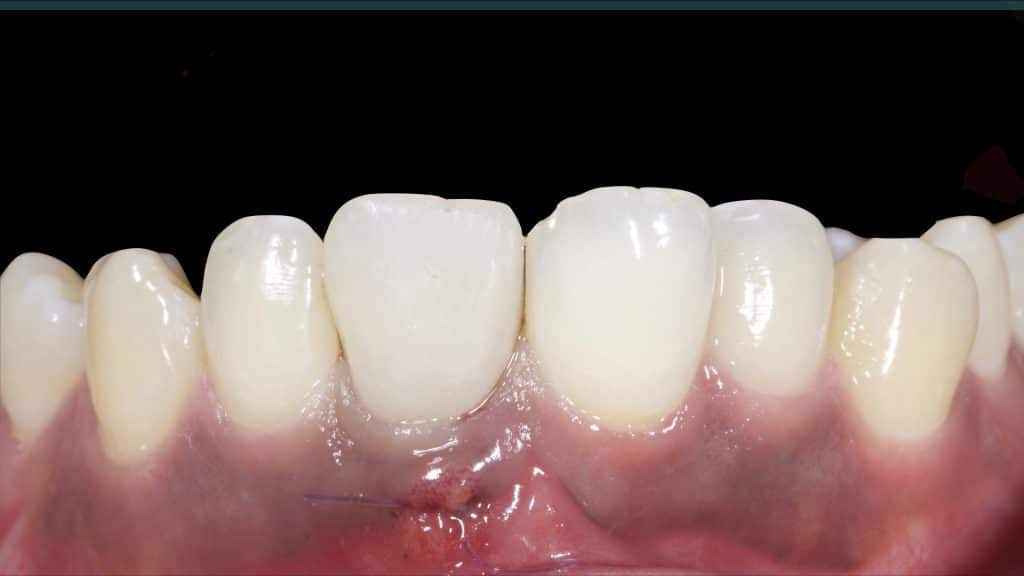
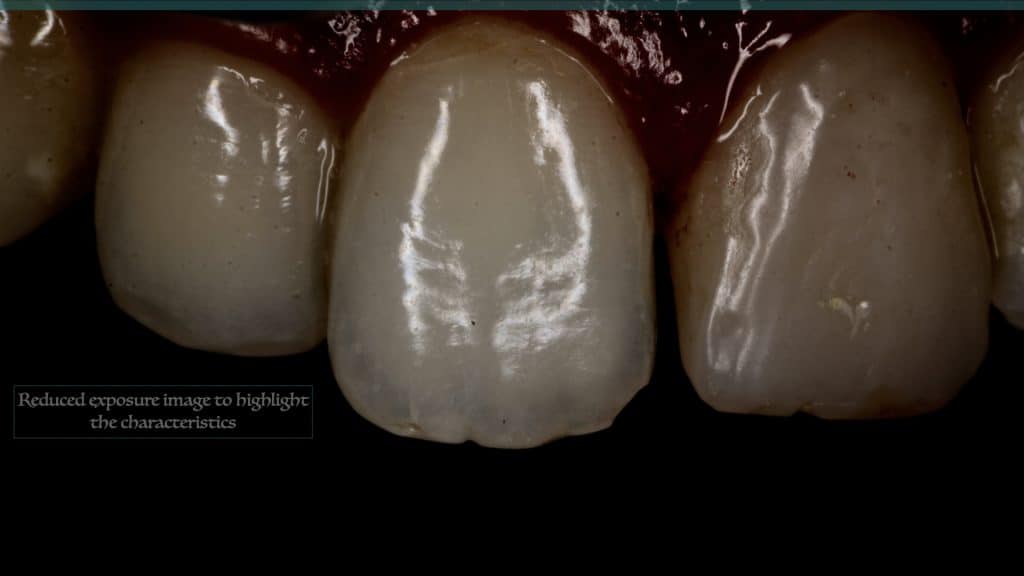
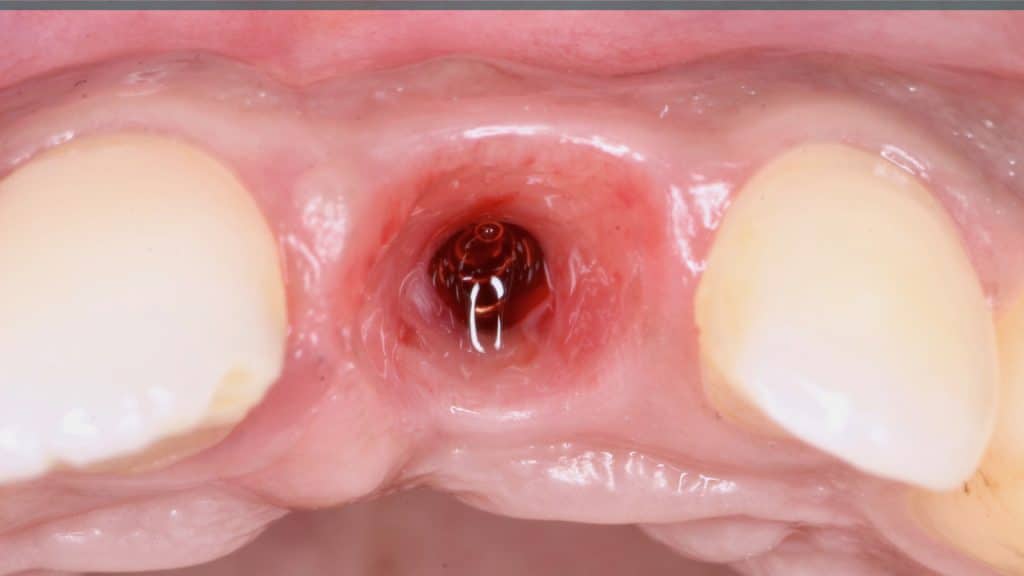
20 days post-op after suture removal
20 days post-op after suture removal
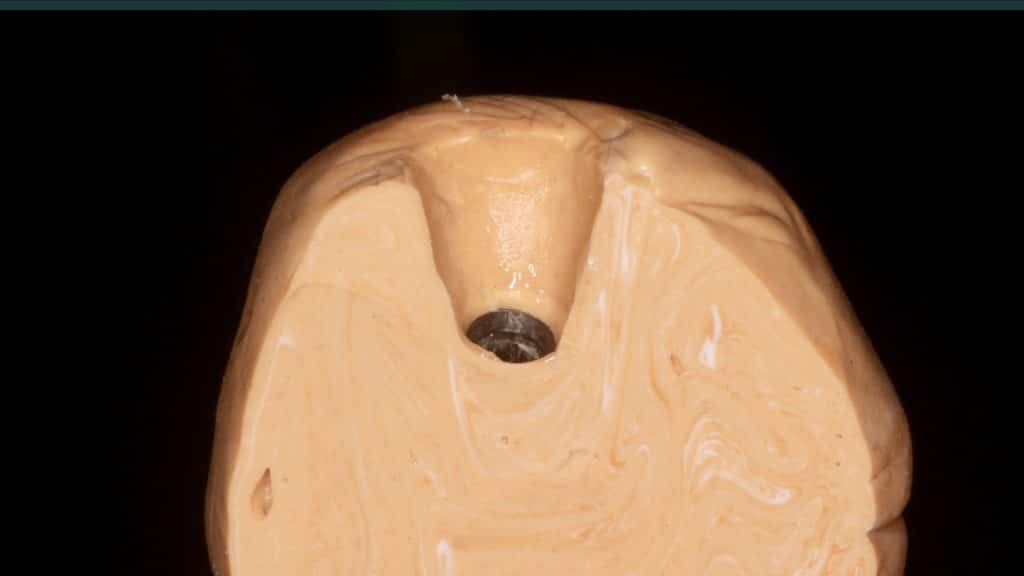




Share on:
